- Abstract
- Industrial production (USD basis (seasonally adjusted))
- Industrial production (USD basis (seasonally adjusted)) (countries around the world)
- Industrial production (USD basis (seasonally adjusted)) (by income, latest year)
- Industrial production (USD basis (seasonally adjusted)) (by income, latest year)
- Reference
Abstract
Industrial production is an important indicator of the health of economic activity and is essential for understanding trends in the global economy. According to April 2024 data, global industrial production will reach USD 1.89 trillion, continuing the upward trend of the past few years. In particular, the growth of manufacturing in emerging market countries is remarkable, with China and India leading the way. These countries are taking advantage of technological innovation and labor cost competitiveness to occupy important positions in international supply chains. Meanwhile, in developed countries, the growth of manufacturing is slowing and the proportion of the service sector is increasing. It should also be considered that tightening environmental regulations and labor shortages are affecting productivity. As digitalization and automation progress, the structure of industrial production is also changing and there is a growing movement toward sustainable growth. Furthermore, recent geopolitical tensions and disruptions to supply chains are also having an impact, and future trends in industrial production require careful monitoring. Overall, industrial production data will continue to be closely watched as an important indicator of changes in the global economy and countries’ competitiveness.
Industrial production (USD basis (seasonally adjusted))
Looking at data on industrial production (USD, seasonally adjusted) from 1991 to April 2024, the world economy has undergone diverse transitions. The $1.89 trillion figure in April 2024 indicates that overall production will have peaked. This growth is due to the development of manufacturing industries, especially in emerging market countries. Low-cost production, particularly in China and India, has increased international competitiveness and led to the development of many industries. Past data shows that the IT bubble in the late 1990s and globalization in the early 2000s boosted industrial production, followed by temporary declines due to the Lehman shock and the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the rapid recovery since 2021 has been driven by a surge in demand and the restructuring of supply chains. Recent trends include the introduction of digital technology and growing environmental awareness, which are transforming production methods and placing greater emphasis on sustainability. With geopolitical tensions and trade frictions affecting supply chains, countries are looking to strengthen their domestic manufacturing industries, which could lead to further transformation of industrial production in the future. As such, industrial production is an important indicator reflecting the dynamics of the global economy, and attention will be focused on future trends.
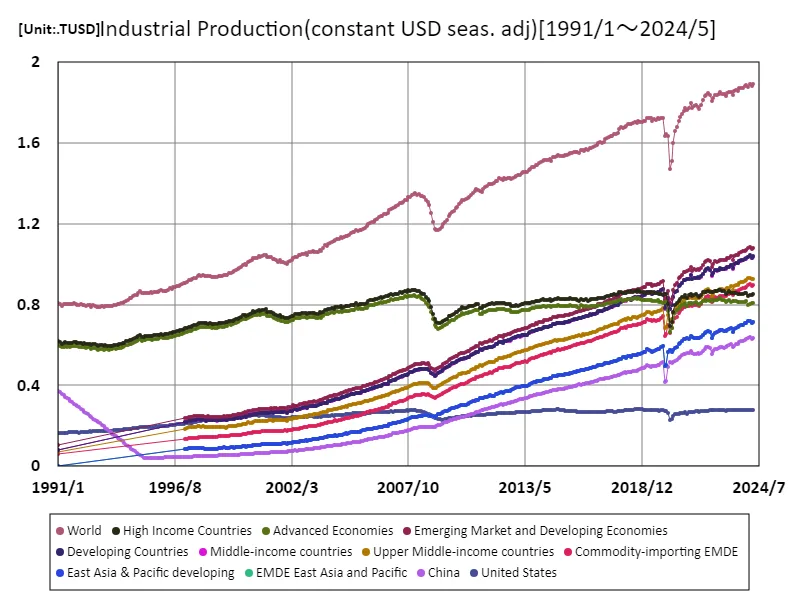

The maximum is the latest one, 1.89TUSD of World
Industrial production (USD basis (seasonally adjusted)) (countries around the world)
Considering Industrial Production (USD, seasonally adjusted) data from 1991 to April 2024, Australian industrial production has notably peaked at 868 GUSD in November 1993 and is currently at around 2.12% of that peak. The decline reflects changes in Australia’s economy, likely resulting from a shift from a resource-dependent economy to one dominated by services. Australia’s economy has strengths in mining and agriculture, but its manufacturing sector is in relative decline. In particular, as trade relations with Asian markets strengthened, outsourcing and imports of manufacturing increased, leading to a decline in domestic industrial production. The economic expansion of the 1990s and the resource boom of the 2000s also had an impact and are considered to be factors in the decline in the competitiveness of the manufacturing industry. In recent years, there has been progress in introducing digital technology and working toward sustainable development, but there are limitations to the recovery of industrial production. Strengthening environmental regulations and labor shortages are also issues, and a shift to a new industrial structure will be required to achieve future growth. Overall, Australian industrial production shows significant variation relative to its historic peak, making economic strategy going forward key.
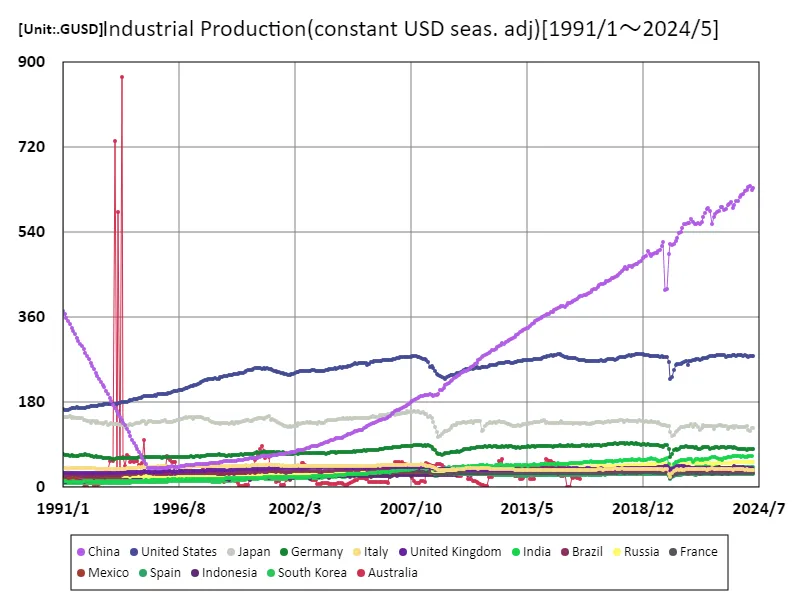

The maximum is 868GUSD[1993年11月] of Australia, and the current value is about 2.12%
Industrial production (USD basis (seasonally adjusted)) (by income, latest year)
Industrial Production (USD, s.a.) data for May 2023 indicates a structural shift in the global economy. Middle-income countries recorded the highest amount at 1.04 trillion USD, with an average of 940 GUSD and a total of 2.93 trillion USD. The results indicate that manufacturing in middle-income countries is growing rapidly, with globalization and technological innovation being cited as key factors. In particular, emerging markets such as China and India are emerging as manufacturing hubs, playing a key role in international supply chains thanks to their low-cost labor and high productivity. Meanwhile, in developed countries, manufacturing has matured and there is a shift towards service industries and high value-added industries. This has resulted in slowing growth in industrial production and challenges such as labor shortages and environmental regulations. Recent data also reflects the ongoing recovery from the pandemic, rising energy costs and geopolitical tensions impacting production. The expansion of industrial production in middle-income countries signals a shift in the global economic balance and will have a major impact on future economic strategies and international competitiveness. Overall, industrial production is an important indicator that highlights the economic characteristics and challenges of each region.
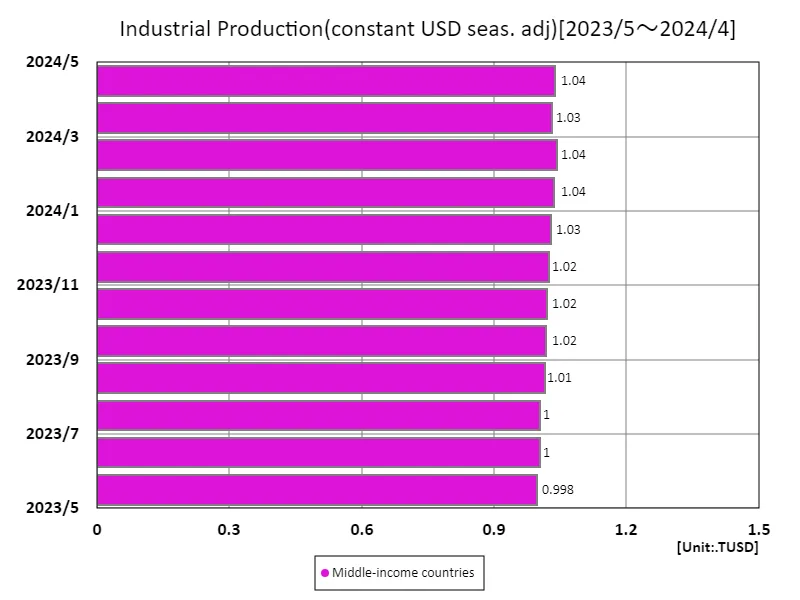

The maximum is 1.04TUSD[2024年2月] of Middle-income countries, and the current value is about 99.5%
Industrial production (USD basis (seasonally adjusted)) (by income, latest year)
Industrial Production (USD, s.a.) data for April 2024 shows diverse changes in the global economy. Middle-income countries recorded the highest figure of 1.04 trillion USD, for an overall total of 2.82 trillion USD, and an average of 940 GUSD. This trend reflects the rapid growth of middle-income countries as manufacturing centres in particular. Middle-income countries are growing as countries including China and India take advantage of low-cost labor and abundant resources to become more internationally competitive. This makes the role of middle-income countries in global supply chains increasingly important. In particular, the expansion of the manufacturing industry is a factor supporting economic growth and also contributes to job creation. Meanwhile, in developed countries, the growth of the manufacturing sector is slowing, and there is a shift towards high value-added industries and the service sector. Along with this, labor shortages and environmental regulations are posing challenges to the manufacturing industry. We also cannot ignore the impact that recent geopolitical tensions and energy price fluctuations are having on supply chains. Overall, industrial production data reflects regional economic characteristics and changes, and is an important indicator for future international economic strategies. The growth of middle-income countries has the potential to change the balance of the global economy and is therefore a factor to watch.

The maximum is 1.04TUSD of Middle-income countries, the average is 1.04TUSD, and the total is 1.04TUSD



Comments