Abstract
In the global economy, the growth rate of agricultural, forestry and fisheries production is an important indicator. Data for 2023 shows Belize showing a high growth rate of 22.6%. This suggests that Belize is exploring new opportunities and increasing productivity in agriculture and fishing. Meanwhile, other countries are also increasing their growth rates through technological innovation in agriculture and the promotion of sustainable farming practices. This trend is driven by increasing global demand for food and increased adaptability to climate change. Countries with high growth rates in agriculture, forestry and fisheries have a positive impact on the economy as a whole, contributing to increased employment and incomes. Going forward, the promotion of sustainable agriculture and advances in technological innovation will likely remain key factors driving growth in the agricultural sector.
Agriculture, forestry and fisheries, annual growth rate
The growth rate of agriculture, forestry and fisheries has played an important role in the global economy. Looking at the data, particularly from 1961 to 2023, there is considerable variation in the growth of agriculture, forestry and fisheries in each country. Morocco’s growth rate was notable for its peak of 73.6% in 1996, but has now fallen to 8.82%. Although this was a temporary anomaly, the growth rate has since shown stability. Global growth rates in agriculture, forestry and fisheries are being influenced by technological innovation and investment, and in developing and emerging countries, the promotion of sustainable agriculture is driving growth. Meanwhile, in developed countries, advanced technology and improved efficiency underpin productivity. Agricultural growth remains important as it is directly linked to gross domestic product (GDP) and is deeply related to employment and food security. As we continue to address challenges such as climate change and population growth and need to promote sustainable agriculture, the growth rates of agriculture, forestry and fisheries are expected to remain stable. International cooperation and technology sharing will be key to the future of agriculture.
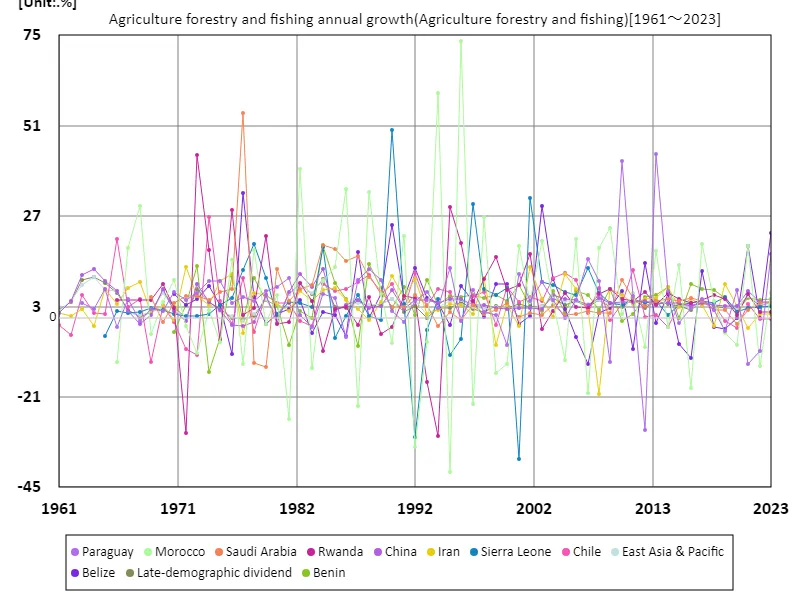

The maximum is 73.6%[1996] of Morocco, and the current value is about 8.82%
Agriculture, forestry and fisheries, annual growth rates (worldwide)
The growth rates of agriculture, forestry and fisheries have shown large fluctuations throughout the data period from 1961 to 2023. Morocco’s growth rate, in particular, was record high at 73.6% in 1996, but declined to 8.82% in the following decades. The fluctuations are due to the impact of climate change and weather conditions on agriculture and fishing, as well as changes in domestic and international economic policies. Generally, growth rates in developing and emerging countries are driven by improvements in agricultural productivity and technological innovation. This has strengthened food security in the country and supported economic activity in rural areas. Meanwhile, developed countries are seeing relatively stable growth as their agricultural sectors move towards more efficient and sustainable production practices. Growth rates of agriculture, forestry and fisheries vary greatly from country to country, but overall there is a need to promote sustainable agriculture in response to increasing global food demand and population growth. In the future, efforts to address climate change and the sustainability of natural resources will become increasingly important, and international cooperation will be necessary. Agricultural development will continue to play a vital role in economic growth and social stability.
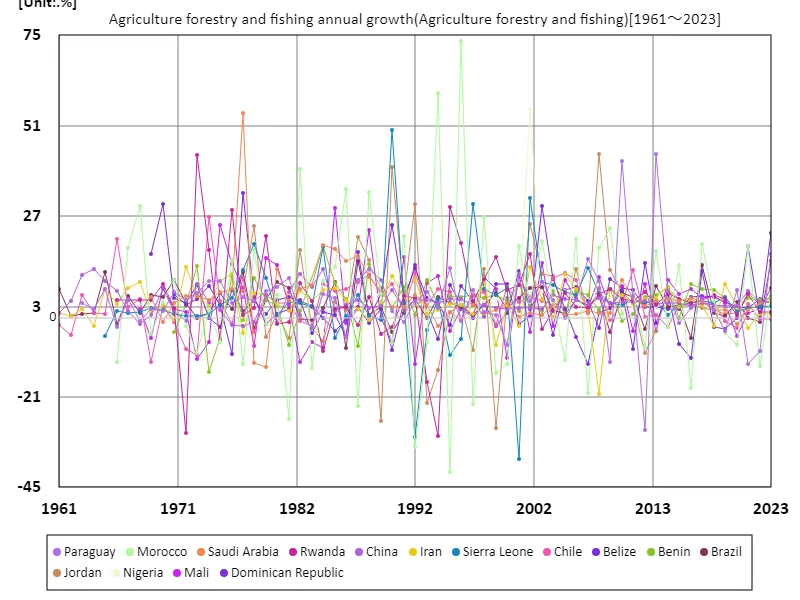

The maximum is 73.6%[1996] of Morocco, and the current value is about 8.82%
Agriculture, forestry and fisheries, annual growth rate (worldwide, latest year)
There is a big difference in the growth rates of agriculture, forestry and fisheries when looking at data for 2023. Hungary’s high growth rate of 68.7% was the largest overall, reflecting a temporary increase due to certain factors. Meanwhile, the overall average growth rate was 2.21%, suggesting long-term stability. These differences are due to national and regional agricultural policies, economic situations, and climatic conditions, which have a significant impact on growth rates. Reasons for the low average growth rates of agriculture, forestry and fisheries include the maturity of the agricultural sector in developed countries and advances in technological innovation. In contrast, in developing and emerging countries, improvements in agricultural productivity and the development of agricultural infrastructure are driving growth rates. Additionally, the overall combined growth rate of 340% indicates that agriculture has been a sustained growing part of the economy, but there have also been significant fluctuations and challenges along the way. In the future, promoting sustainable agriculture will become even more important as we face the effects of climate change and population growth. It is expected that international cooperation and technology sharing will contribute to improving agricultural productivity and improving food security. While agriculture, forestry and fisheries continue to play an important role in the global economy, their sustainable development will be a challenge in the future.
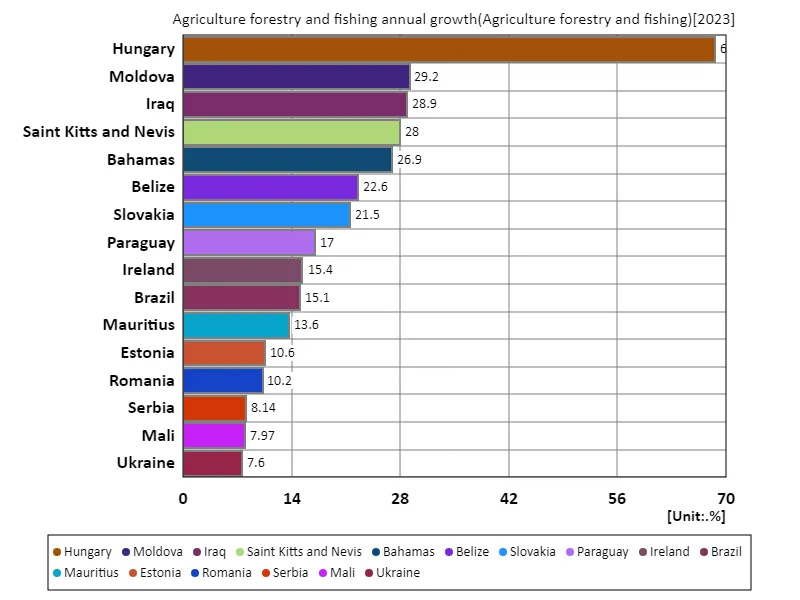

The maximum is 68.7% of Hungary, the average is 2.26%, and the total is 346%
Agriculture, forestry and fisheries, annual growth rate (region, latest year)
The latest data on the growth rate of agriculture, forestry and fishing in the world (2023) shows that Central European and Baltic countries recorded the largest growth rate (8.94%). This indicates that agricultural and fishing activities in particular are increasing in the region. Meanwhile, the overall average growth rate was 1.69%, reflecting relatively modest growth in the agricultural sector across the world. As the combined growth rate of 21.9% shows, there is considerable variation in growth rates across countries and regions. A notable feature of the growth rates of agriculture, forestry and fisheries is the promotion of improved agricultural productivity in developing and emerging countries. This has made the agriculture sector a key driver of economic growth, contributing to job creation and improving food security. Meanwhile, developed countries are making efforts to stabilize growth rates through technological innovation in agriculture and the introduction of sustainable production methods. Future challenges include strengthening the agricultural sector, which is vulnerable to the effects of climate change and natural disasters. Furthermore, promoting sustainable agriculture will become increasingly important in order to meet increasing food demand and population growth. International cooperation and technology sharing are essential to support the growth of agriculture, forestry and fisheries, which will hopefully lead to a more sustainable future for agriculture around the world.
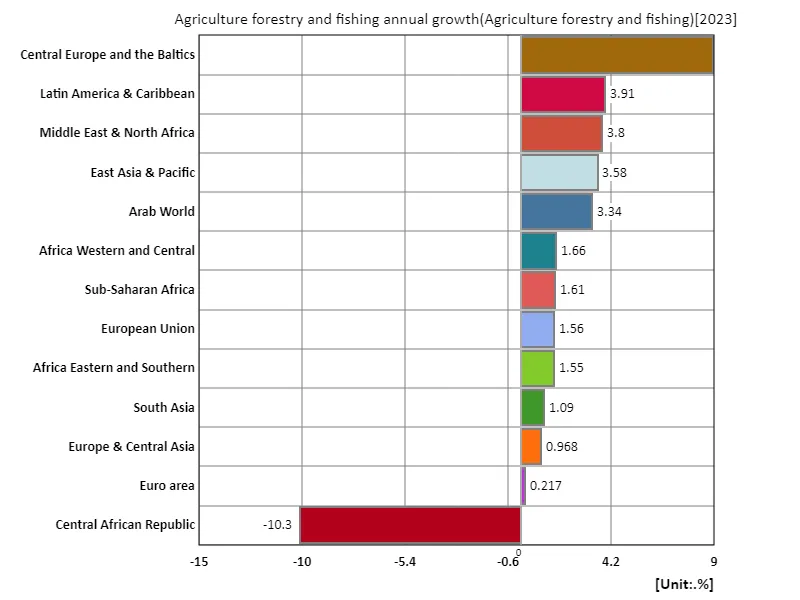

The maximum is 8.94% of Central Europe and the Baltics, the average is 1.69%, and the total is 21.9%



Comments