- Abstract
- Unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 (percentage of total male labor force)
- Unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 (percentage of total male labor force) (worldwide)
- Unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 (percentage of total male labor force) (worldwide, latest year)
- Unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 (percentage of total male labor force) (region, latest year)
- Reference
Abstract
When we consider the employment underemployment rate, we can see that high unemployment rates, especially in a country like Georgia, are influenced by changes in the economic structure and social factors. The 29% figure for 2020 reflects the hard hit the labor market took, in part due to the global pandemic. In Georgia, a lack of diversity in the economy and reliance on certain industries are cited as factors contributing to the high unemployment rate. Another problem is the lack of education and skills among young people, and the fact that human resources that meet the needs of companies are not being developed is leading to a decrease in employment opportunities. To address this issue, it is necessary to reform the education system and develop new industries. In the long term, overcoming these challenges will require improving the quality of jobs and achieving sustainable economic growth.
Unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 (percentage of total male labor force)
Looking back at data from 1983 to 2020, the economic trends indicated by the unemployment rate for men (aged 15-64) vary widely from country to country. Kosovo’s 42.9% figure in 2008 was particularly notable as a result of the economic crisis and political instability. During this period, Kosovo declared its independence, but its weak economic base led to a sharp rise in unemployment. Kosovo’s current figure of 64.3% reflects regional characteristics and the impact of past economic policies. Causes of unemployment include lack of education and vocational training, lack of economic diversification, and lack of foreign investment. High unemployment rates, especially among young people, also affect social stability and are an obstacle to long-term economic growth. Overall, data from the past few decades show the impact of economic crises and political developments on labor markets, highlighting the fragility and resilience of economies that vary across countries. Going forward, reforms to the labor market and improvements to the education system will be important in order to achieve sustainable growth.
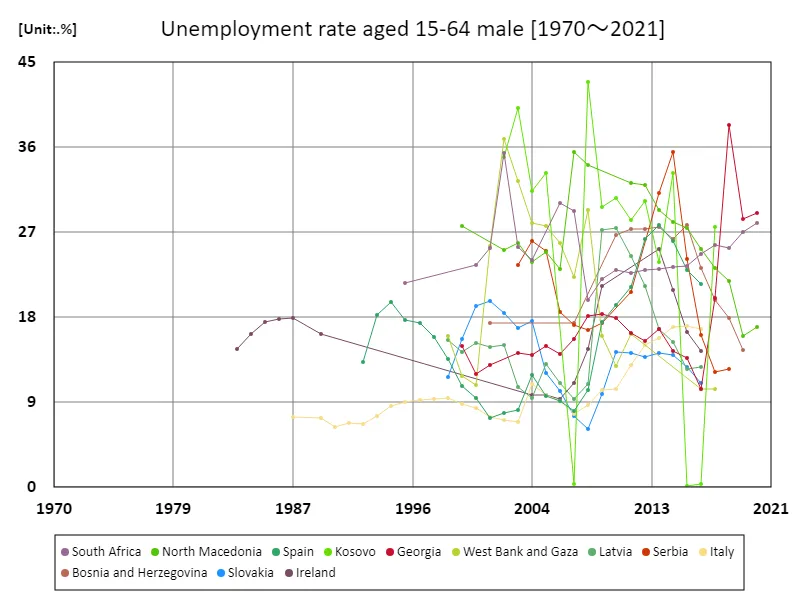

The maximum is 42.9%[2008] of Kosovo, and the current value is about 64.3%
Unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 (percentage of total male labor force) (worldwide)
Looking at data from 1981 to 2021, the unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 is particularly striking in the case of Kosovo. Kosovo recorded a population density of 42.9% in 2008, but has continued to face economic instability since then, with the current rate standing at 64.3%. This high unemployment rate is due to a weak economic foundation, political instability, and an underdeveloped education system. Rising unemployment is particularly severe among young people, making it difficult for them to enter the labor market. Historical data highlights the impact of economic crises on labor markets and the vulnerabilities that come with dependency on certain industries. In countries like Kosovo, the lack of foreign direct investment has prevented the economy from diversifying and creating jobs. Going forward, structural reform of the labor market and the enhancement of education and training will be necessary, with particular emphasis on strengthening vocational training programs. Improving the quality of jobs will be key to achieving sustainable economic growth.
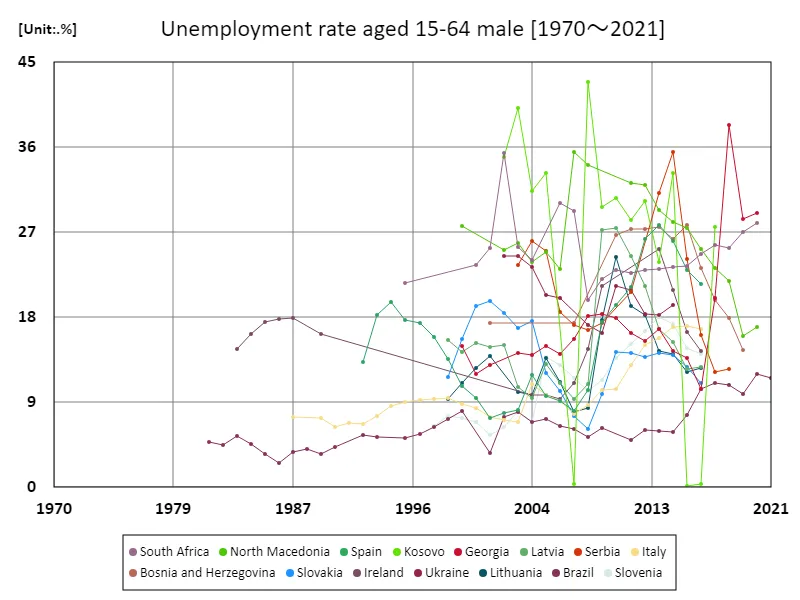

The maximum is 42.9%[2008] of Kosovo, and the current value is about 64.3%
Unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 (percentage of total male labor force) (worldwide, latest year)
Based on 2021 data, the unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 is highest in Gambia at 21.5%, with the overall average at 8.36%, totalling 134%. The Gambia’s high unemployment rate stems from its fragile economy and its reliance on agriculture, making it particularly difficult for young people to enter the labor market. The data shows that unemployment rates vary widely across countries, reflecting the influence of economic policies and social factors. While many countries have shown a trend of declining unemployment rates in line with economic growth, there are countries such as The Gambia where high unemployment rates persist. This reflects a lack of quality education, vocational training and inadequate infrastructure for job creation. The total figure of 134% also indicates that a certain percentage of the population is unemployed, as is the overall labor force ratio, including both men and women. To address this, labor market reforms and strengthening education systems are essential. In order to achieve sustainable economic growth, expanding employment opportunities and improving the quality of the labor force are important issues.
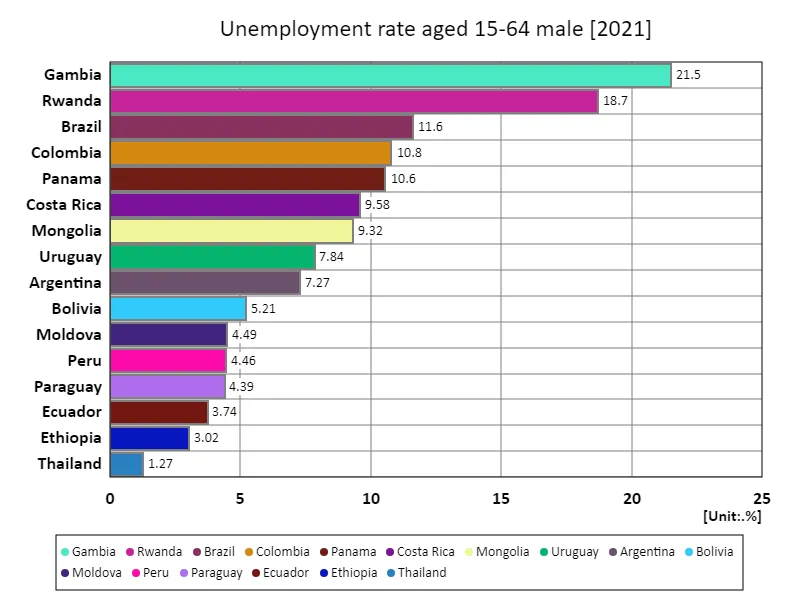

The maximum is 21.5% of Gambia, the average is 8.36%, and the total is 134%
Unemployment rate for men aged 15-64 (percentage of total male labor force) (region, latest year)
Analysing the unemployment rate for men aged 15-64, based on data from 2008, the Central African Republic recorded the highest rate at 21.9%, with the same figures for the overall average and total. The underlying causes of this high unemployment rate are thought to be economic instability, political turmoil, and a lack of social infrastructure. In particular, the Central African Republic is rich in resources, but civil war and poverty are hindering economic development, and youth unemployment is a serious problem. These countries also have underdeveloped labour markets and limited access to education and training, resulting in a poor quality workforce. The year 2008 was also affected by the global financial crisis, which led to an increase in the overall unemployment rate. Data from this period underscores the importance of economic fragility and resilience to crises. In order to achieve sustainable economic growth, it is essential to improve the labor market, strengthen the education system, and develop infrastructure, and it can be said that expanding employment opportunities for young people is a particularly urgent task.
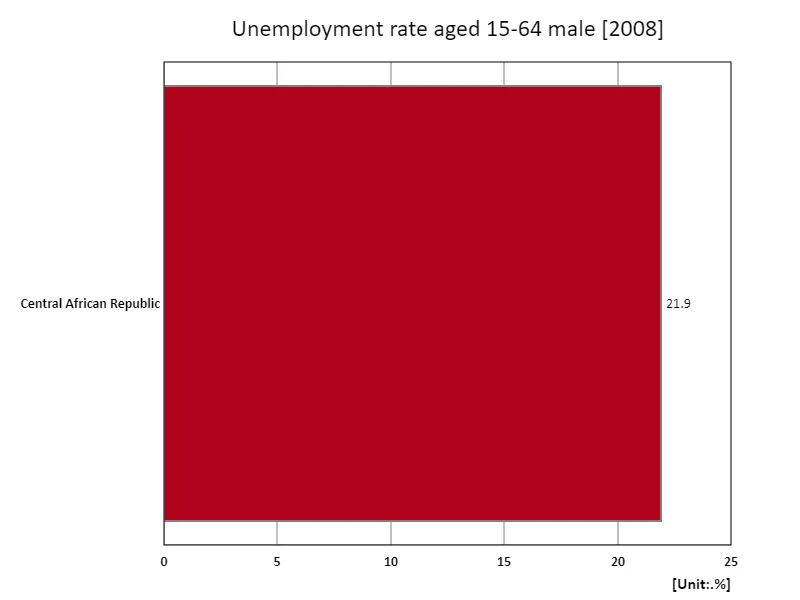

The maximum is 21.9% of Central African Republic, the average is 21.9%, and the total is 21.9%



Comments