Abstract
Rural population trends have important implications for the global economy and social structure. Over the past few decades, the rural population has been declining due to urbanization, but is projected to reach 3.1 billion by 2050. This increase is due to higher fertility rates in rural areas in some countries and slower migration to cities in other areas. A growing rural population means there is a need to increase agricultural productivity, develop the local economy or improve living standards. On the other hand, overcrowding in rural areas and slow infrastructure development may also give rise to social challenges. The key to the sustainable development of rural areas is the introduction of technological innovation and regional development policies.
Rural population
The evolution of rural population between 1960 and 2050 reflects the evolution of the global economy and urbanization. In 1960, the rural population was around 2.2 billion, but by 2020 it had peaked at 3.44 billion. This increase was due to many areas being dependent on agriculture. However, with the recent urbanization and economic development, the rural population has been declining. The current rural population is only 90.2% of its peak. Migration to cities and changes in industrial structure are the main factors behind this decline. In rural areas, although there has been an increase in countries with high birth rates and in developing countries, overall agricultural mechanization and efficiency are progressing along with population outflow. In the future, population redistribution and sustainable agricultural development will be important.
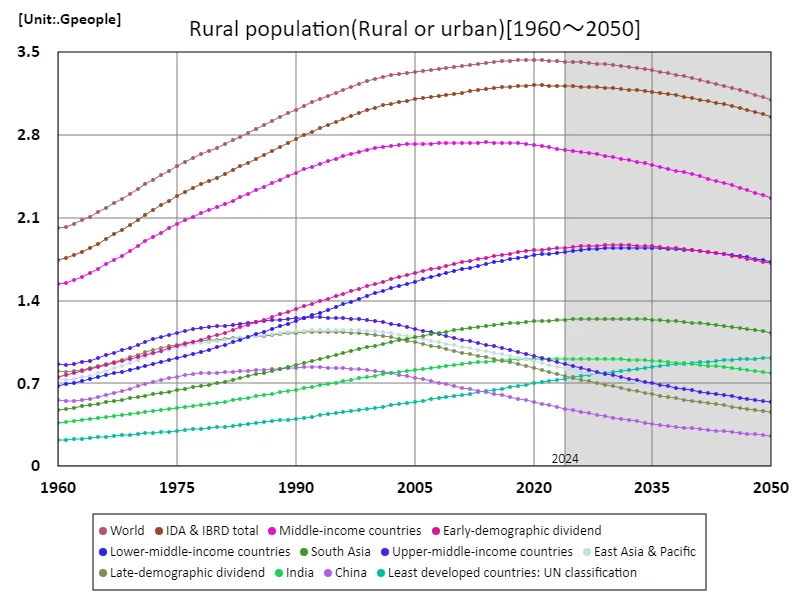

The maximum is 3.44Gpeople[2020] of World, and the current value is about 90.2%
Rural population (worldwide)
The change in India’s rural population between 1960 and 2050 strongly reflects the impacts of urbanization and economic growth. In 1960, India’s rural population was around 550 million, but by 2026 it was expected to reach a peak of 911 million. This rapid growth is attributable to an agricultural-based economic structure and high birth rates. However, with increasing urbanization and economic development, India’s rural population is on the decline. The current rural population is 86.5% of its peak, primarily due to migration to urban areas. In addition, agricultural mechanization and efficiency are increasing, reducing employment opportunities in rural areas. In the future, sustainable development of rural areas and economic diversification will become important issues, and balanced growth between urban and rural areas will be required.
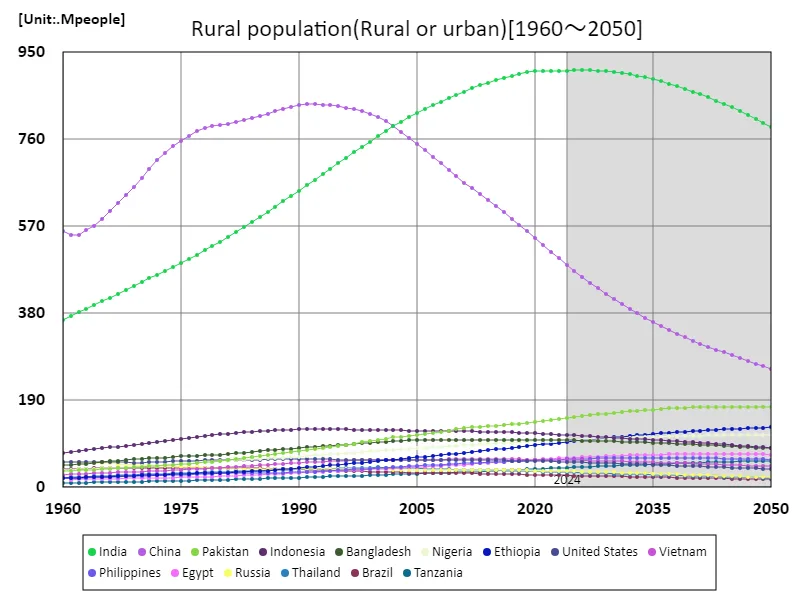

The maximum is 911Mpeople[2026] of India, and the current value is about 86.5%
Rural population (worldwide, latest year)
As per the data for 2050, the world’s rural population will total 2.96 billion, with India having the largest rural population at 788 million. Over the past few decades, the trend has been for rural populations to decline due to increasing urbanization and economic growth. In particular, in developed countries, there is a significant shift in population to cities, while the rural population is decreasing relatively. On the other hand, India and some other developing countries still have large rural populations and large areas that depend on agriculture. India has a large rural population that has a strong influence on the region’s economy and social structure, despite increasing urbanization. The average rural population of 15.3 million indicates that rural areas exist at a certain size in each country and that agriculture and local economies are important. The challenge going forward is how to improve living standards and achieve sustainable development in rural areas.
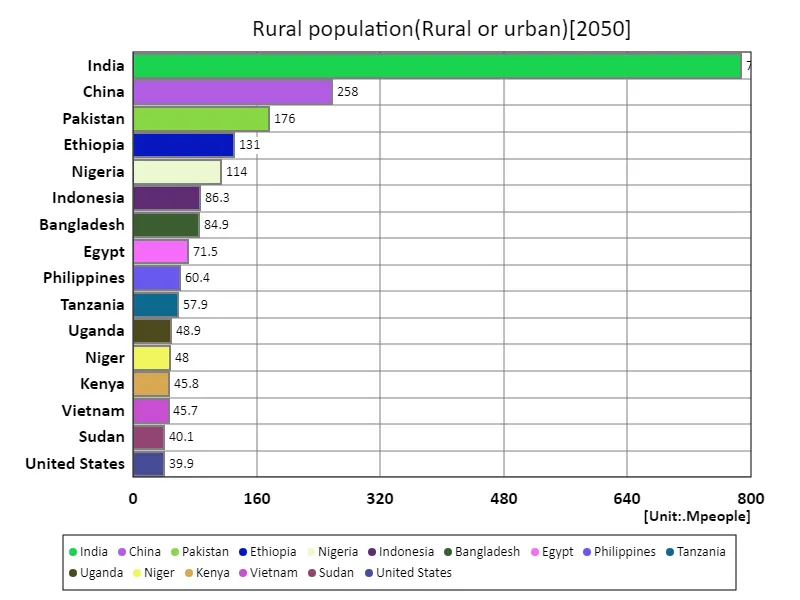

The maximum is 788Mpeople of India, the average is 15.3Mpeople, and the total is 2.94Gpeople
Rural population (region, latest year)
According to data for 2050, the world’s rural population will total 4.28 billion, of which South Asia will have the largest rural population at 1.13 billion. The region’s large rural population reflects an economic structure that remains dependent on agriculture and a high birth rate. The trend over the past few decades has been one of increasing urbanization and a decline in the rural population in many countries, although in developing regions such as South Asia this trend has been more moderate and rural populations remain large. The global average rural population is 285 million, which again highlights the importance of rural areas, despite the impacts of urbanization. The large rural population plays a central role in agricultural production and the local economy, making the development of rural areas and improving living standards important issues. Additionally, population growth and decline in rural areas also affect food security and regional disparities. Promoting sustainable agriculture and revitalizing the economies of rural areas will be key in the future.
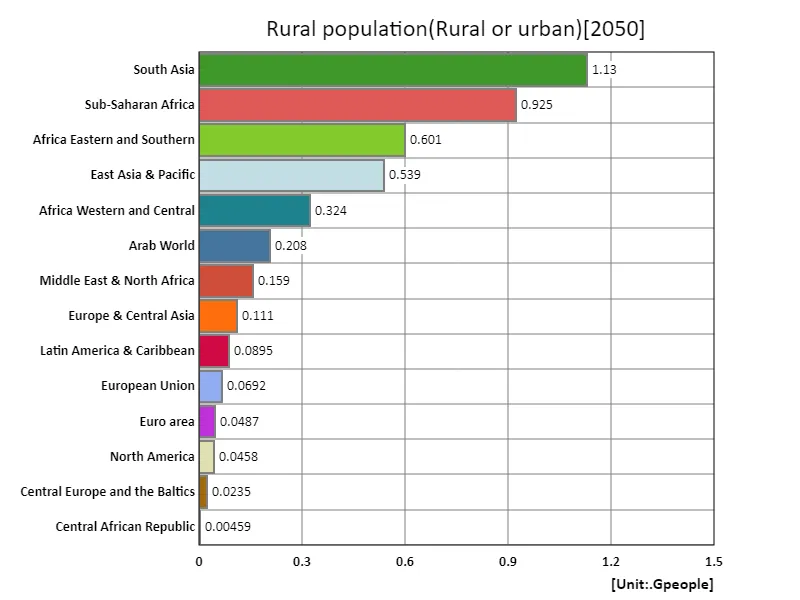

The maximum is 1.13Gpeople of South Asia, the average is 285Mpeople, and the total is 4.28Gpeople



Comments