Abstract
Low-income countries with high annual rural population growth rates experience high population growth, which has multiple economic and social implications. In particular, projections for 2050 show that the annual growth rate of rural population in low-income countries will reach 536%. This rapid increase is mainly due to high birth rates and overpopulation in rural areas. Rural areas face difficulties in achieving economic development due to lack of education and health infrastructure and poor quality of life. This results in a growing rural population that is not provided with sufficient resources or employment opportunities, perpetuating the cycle of poverty. On the other hand, an increase in the rural population can also contribute to agricultural production and the development of the local economy, but for this to happen, the spread of education and technology and the development of infrastructure are essential. In addition, rapid population growth could increase migration pressure to urban areas, leading to overcrowding and increased strain on urban infrastructure. Therefore, policies that aim for balanced growth between rural and urban areas are important to achieve sustainable development.
Annual growth rate of rural population
Based on data from 1961 to 2050, there will be notable changes in urban and rural demographics. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) recorded an impressive annual rural population growth rate of 17% in 1969, but it has since declined sharply, currently standing at -6.54%. This change is largely due to the UAE’s rapid urbanization and economic development. From the 1960s to the early 1970s, many countries experienced high rates of rural population growth due to high birth rates and economic structures that were highly dependent on agriculture. However, with economic development and urbanization, rural-to-urban migration accelerated and the growth rate of the rural population gradually declined. The development of the oil industry has led to rapid urban growth and a decline in rural population, particularly in countries like the UAE. As a result of this urban concentration, the population growth rate in rural areas has fallen significantly from its peak, and they are now facing a decline in population. This has resulted in a slowdown in the growth rate of rural population around the world, with rural populations declining as urbanization progresses.
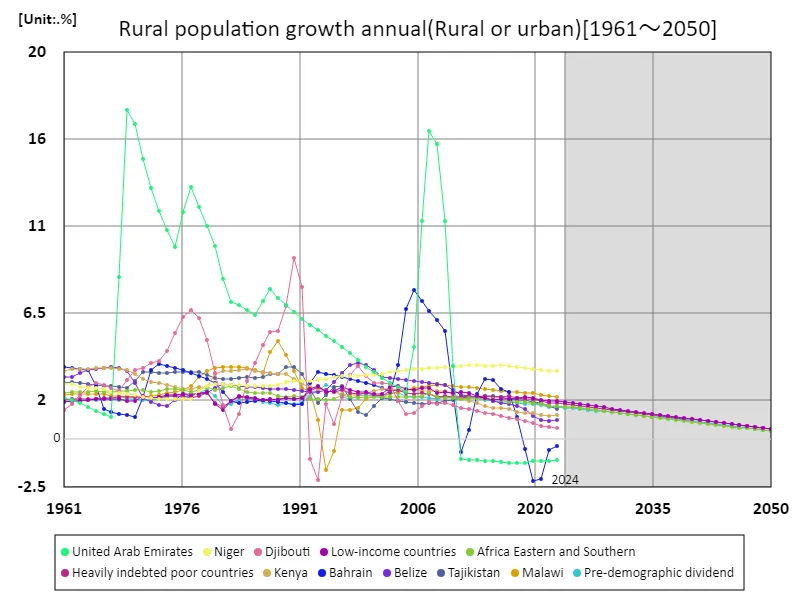

The maximum is 17%[1969] of United Arab Emirates, and the current value is about -6.54%
Annual rural population growth rate (worldwide)
Looking at data from 1961 to 2023, there is a notable change in the annual growth rate of rural population. In particular, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) recorded an extremely high rural population growth rate of 17% in 1969, but has since experienced a rapid decline, and is currently experiencing negative growth of -6.54%. This change is due to the UAE experiencing rapid urbanization and economic growth. During the 1960s and early 1970s, many countries experienced significant rural population growth. The background to this was a high birth rate and an agricultural-centered economic structure. However, with the development of the economy and the progress of urbanization, migration from rural areas to cities increased and the growth rate of the rural population gradually declined. In the UAE in particular, the development of the oil industry has fuelled rapid urban growth while reducing rural populations. As such, amid economic development and urbanization, the rate of rural population growth is declining around the world, and there is a trend for rural populations to decline. Urban concentration and economic changes are having a major impact on rural population dynamics.
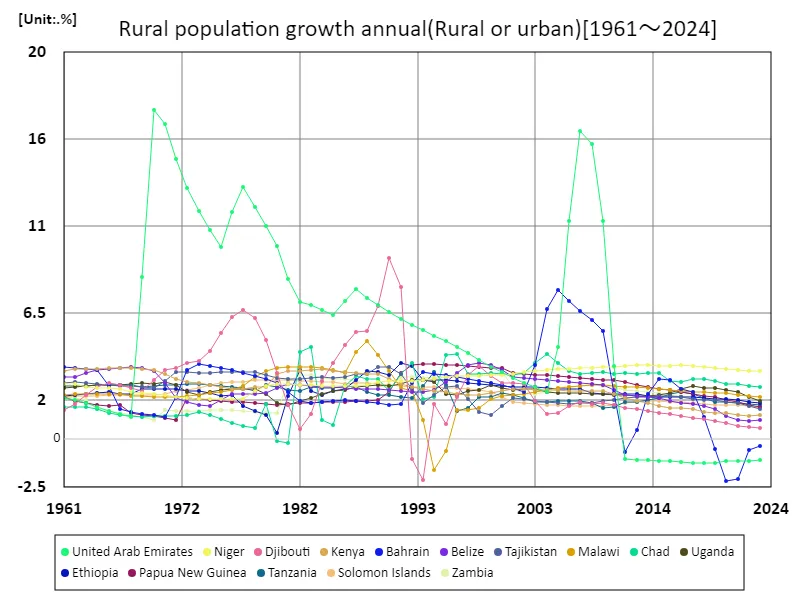

The maximum is 17%[1969] of United Arab Emirates, and the current value is about -6.54%
Annual rural population growth rate (world countries, latest year)
According to 2024 data, the annual rural population growth rate is the highest in Venezuela at 1.36%, with an average of 506m% and a total of 4.55%. These figures reveal several important characteristics and trends about rural population dynamics. Over the past few decades, rural population growth rates have been gradually declining in many countries. The main factors behind this are urbanization and changes in the economic structure. As the population moves from rural to urban areas, the rate of growth of the rural population is declining and urban concentration is becoming more pronounced. On the other hand, Venezuela’s figure of 1.36% indicates a relatively high growth rate, suggesting that population growth in rural areas continues at a steady rate. This may be due to improved living conditions in rural areas and high dependency on agriculture. Additionally, the data of 506m% average and 4.55% total may reflect bias in the overall growth rate or sharp fluctuations in certain regions. Overall, the annual growth rate of rural population varies widely across regions, with urbanization and economic factors deeply influencing its dynamics.
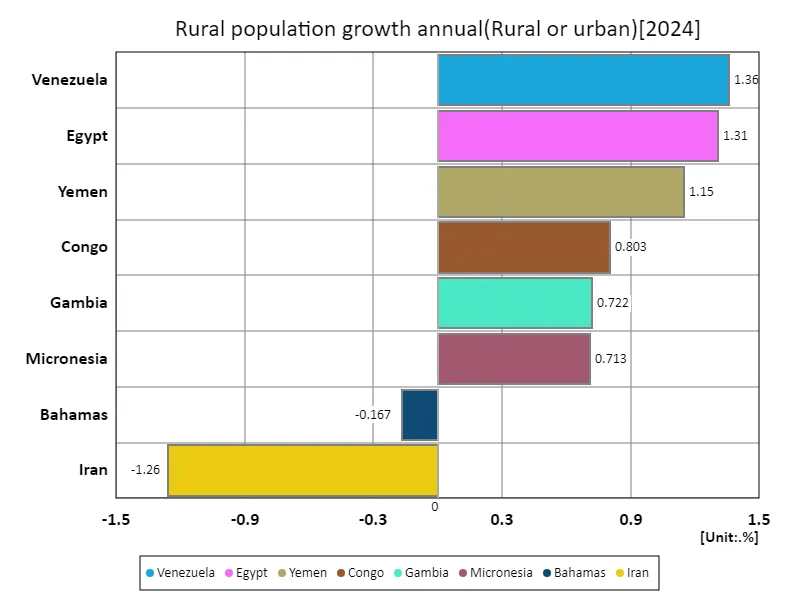

The maximum is 1.36% of Venezuela, the average is 579m%, and the total is 4.63%
Annual rural population growth rate (region, latest year)
Data for 2050 show that annual rural population growth rates vary widely across regions. Eastern and Southern Africa recorded the highest increases of up to 395m%, compared to an overall average of -982m% and a total of -13.8%. These extreme figures reveal some striking trends about rural population dynamics. First, the high growth rates in eastern and southern Africa indicate continued rural population growth. This is due to factors such as a high birth rate, a local economy dependent on agriculture, and improved survival rates due to improved medical care. However, it is also necessary to consider the possibility that the extremely high growth rate in this region may be due to some special factors in the measurement methods or data handling. On the other hand, the overall average shows a significant decrease of -982% making it clear that the rural population is on a downward trend worldwide. The main factors behind this are the progress of urbanization, increased migration from rural areas, and changes in the economic structure. In particular, in developing countries, as urban areas expand, population migration from rural areas to cities is increasing. The result is a decline in rural populations around the world and a sharp decline in rural population growth rates. The data highlights differences in rural demographics across regions and how increasing global urbanization is contributing to rural depopulation.
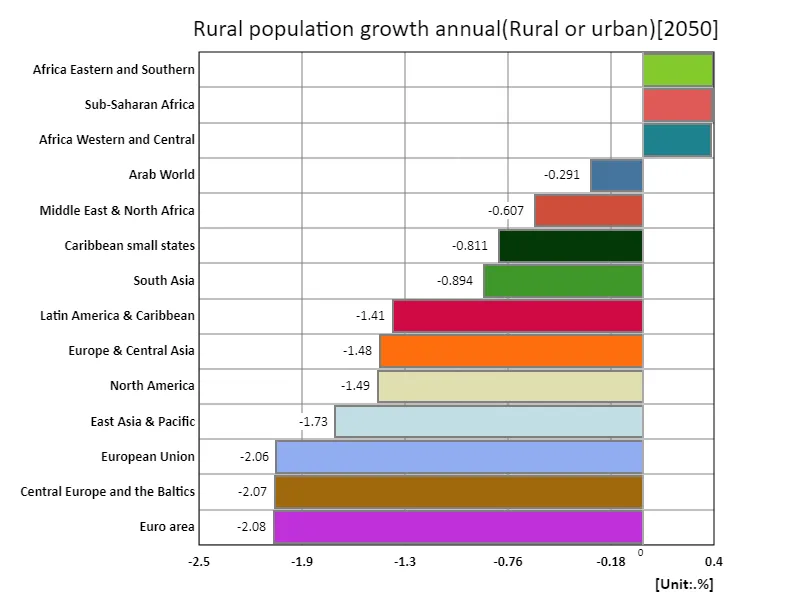

The maximum is 395m% of Africa Eastern and Southern, the average is -982m%, and the total is -13.8%



Comments