Abstract
There are several common trends among countries and regions with high urban populations (percentage of total population). Bermuda will be 100% urban by 2050, meaning that almost all residents will be concentrated in urban areas. Data to date shows that urbanization is generally closely associated with economic development and improved living standards. The concentration of population in cities increases economic opportunities and contributes to improving the efficiency of society by concentrating the development of infrastructure and the provision of services. On the other hand, urbanization also brings with it challenges such as housing problems, traffic congestion, and environmental issues. The example of Bermuda also calls for a deeper look into the impact of urban development on the overall development of the region and the challenges that come with it.
Urban population (percentage of total population)
Bermuda’s urban population (as a percentage of total population) in 1960 was 100%, indicating that at that time the entire population was concentrated in urban areas. This is the result of Bermuda being a relatively small island nation, and land constraints have led to extreme urbanization. This trend can be seen as symbolic of the progress of urbanization around the world. Since the 1960s, urbanization has accelerated in many countries, with the population concentrating in urban areas along with economic growth and industrial development. Rural-urban migration is particularly prevalent in developing countries, driven primarily by improving living standards and increasing job opportunities. On the other hand, issues such as urban overcrowding, environmental problems, and increasing burdens on infrastructure have become apparent in recent years. As an extreme example of urbanization, Bermuda serves as a valuable case study for understanding the characteristics and impacts of urbanization in other regions.
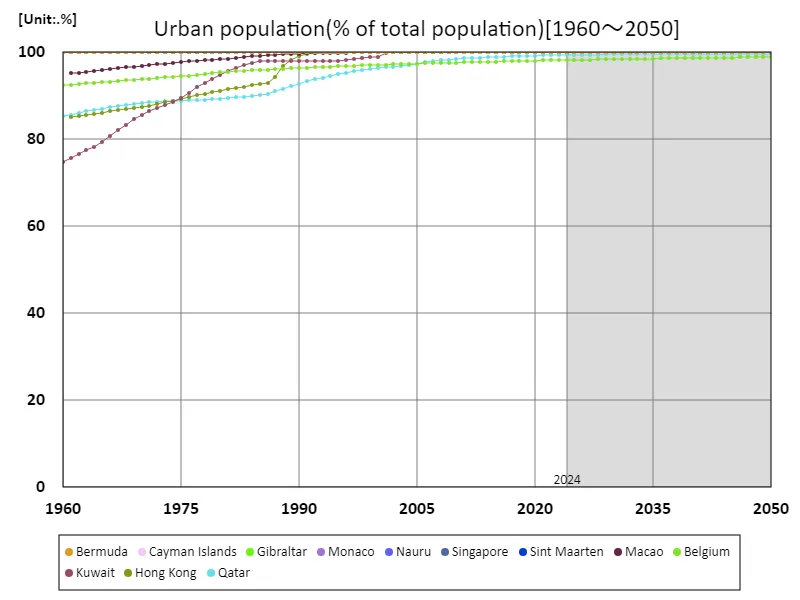

The maximum is 100%[1960] of Bermuda, and the current value is about 100%
Urban population (percentage of total population) (countries around the world)
The data showing that Singapore’s urban population (as a percentage of total population) reached 100% in 1960 indicates that Singapore was already fully urbanized as a city-state at that time. In a small city-state like Singapore, land constraints mean that the population naturally concentrates in urban areas. Since the 1960s, Singapore has undergone rapid economic growth and established itself as an internationally renowned city offering advanced infrastructure and services. This growth strengthened its role as a commercial and financial centre and further promoted urbanisation. Singapore’s 100% urban population is an example of extreme urbanization. Other countries are seeing large changes in the urban-rural population ratio as they urbanize. In many developing countries, rural-urban migration continues, with the proportion of the population living in urban areas increasing. However, it is rare for a country to complete urbanization so quickly, as in Singapore, and its success is due to well-planned urban development and ensuring a high standard of living. Meanwhile, the example of Singapore also shows that increasing urbanization puts increasing pressure on infrastructure and living conditions, underscoring the importance of sustainable urban development.
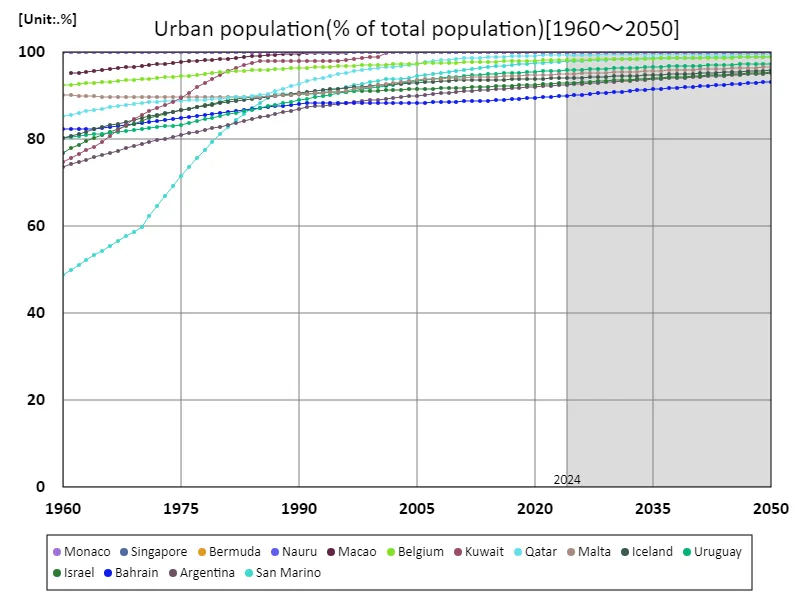

The maximum is 100%[1960] of Monaco, and the current value is about 100%
Urban population (percentage of total population) (worldwide, latest year)
The data showing that Macau’s urban population (as a percentage of total population) will be 100% in 2050 indicates that Macau will be fully urbanized. In a very small area like Macau, the natural tendency is for the population to be concentrated entirely in urban areas. This complete urbanization reflects the fact that limited land availability forces people to concentrate in cities. The average urban population (as a percentage of total population) of 71.1% indicates that although urbanization is increasing worldwide, many people still live in rural or rural areas. The figures suggest that while urban areas are expanding due to economic development and industrial concentration, some areas are still undergoing urbanization. The data showing that the total urban population (ratio to total population) is 13.9% indicates the cumulative urban population ratio, which is an indicator for assessing the progress of global urbanization. While urbanization contributes to economic development and improved living standards, it also brings with it challenges such as overcrowding in urban areas and increased environmental burdens. Overall, while urbanization is expanding economic opportunities, we are entering an era in which measures toward sustainable development are required.
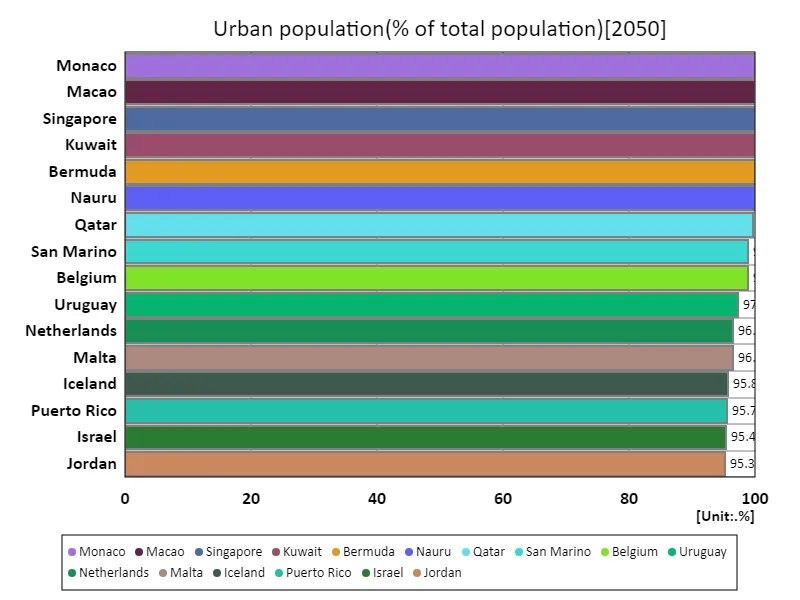

The maximum is 100% of Monaco, the average is 71%, and the total is 13.8k%
Urban population (percentage of total population) (region, latest year)
According to data for 2050, North America’s urban population (as a percentage of the total population) is projected to be a very high 88.9%, indicating that most of North America’s residents will be concentrated in urban areas. A historical trend is that North America has been urbanizing early on, with the economic center shifting to urban areas. The progress of urbanization has contributed to the development of infrastructure, the expansion of services, and an improvement in living standards. The global average urban population share of 70.4% indicates that although urbanization is widespread, many regions still remain rural and rural. In developing countries, urbanization is progressing rapidly, with many people moving to cities in search of better living conditions. The total urban population ratio of 1.06k% is a cumulative value indicating the degree of urbanization, and reflects the overall high progress of urbanization. This figure is an important indicator of the progress of global urbanization. While urbanization enhances economic development and social efficiency, it also brings increasing challenges such as overcrowding and environmental issues. Overall, we can say that we are living in an era where progress in urbanization requires policies that are in harmony with sustainable development.
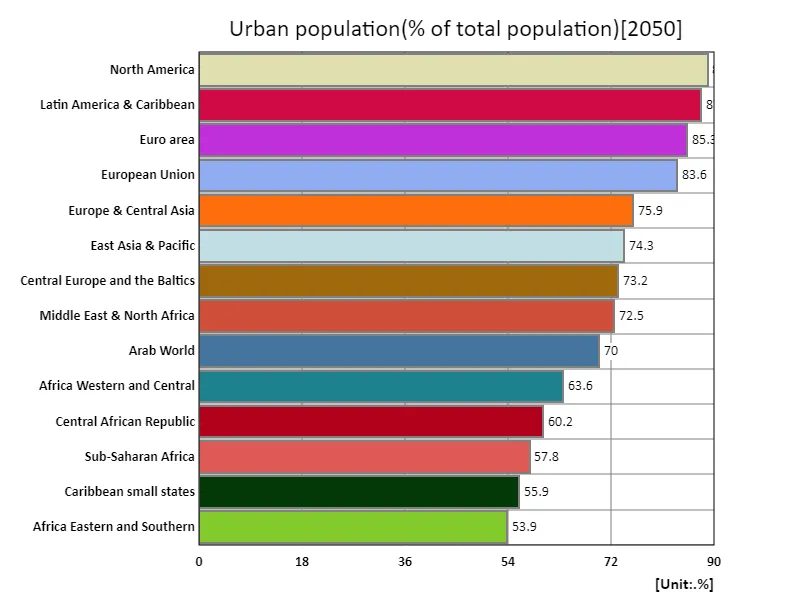

The maximum is 88.9% of North America, the average is 70.4%, and the total is 1.06k%



Comments