Abstract
A high ratio of transportation services (services ratio) indicates a large share of transportation of imported goods. Ethiopia has the highest share at 74.8% because the country’s economy is highly dependent on imports. Developing countries like Ethiopia have limited domestic production capacity and therefore tend to be highly dependent on imports from outside. This will result in a higher ratio of transport services. A trend seen over the past few years is that African countries are becoming increasingly import-dependent, with transportation costs accounting for a large proportion of total import costs, especially in areas with less developed infrastructure. Ethiopia’s high service ratio can be attributed to its economic structure and underdeveloped infrastructure.
Total population
Since 1960, the world’s population has grown dramatically. The world population was approximately 3 billion in 1960 and is expected to reach 9.67 billion by 2050. This increase is mainly evident in developing countries in Asia and Africa. Rapid population growth is associated with economic growth and urbanization, but at the same time it is causing resource depletion and environmental problems. The current population situation, at 100% of its peak, highlights social and economic challenges, particularly the problems of an ageing population and labour shortages. Furthermore, urbanization increases the need for infrastructure development, which leads to widening economic disparities. Going forward, the global economy will require strategies aimed at sustainable development and solving social issues.
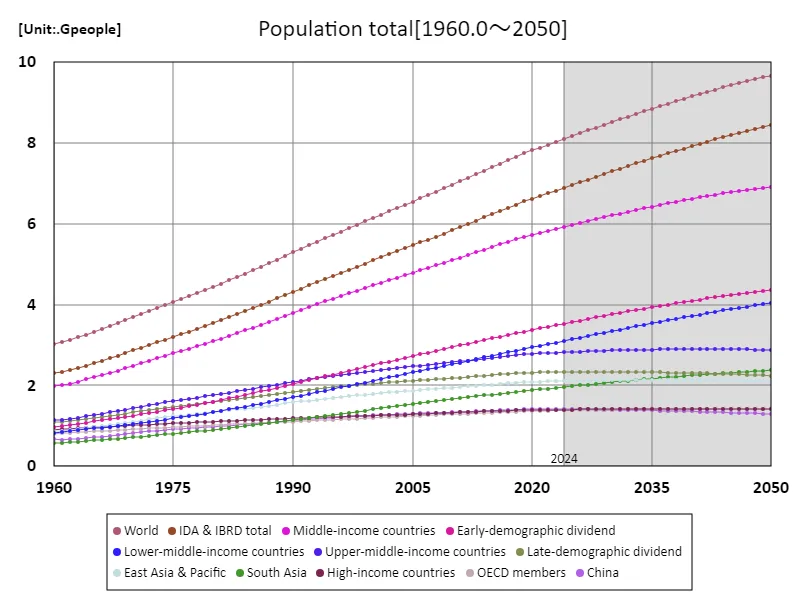

The maximum is the latest one, 9.67Gpeople of World
Total population (worldwide)
India’s population has grown rapidly since 1960 and is projected to reach 1.67 billion by 2050. This will make India the most populous country in the world. Over the past few decades, India has been characterised by a high birth rate and a young age group, which have been major drivers of economic growth. As urbanization progresses, the labor supply is increasing and the consumer market is expanding, but at the same time, demand for education, medical care, and infrastructure is also increasing. India’s rapidly growing population offers economic opportunities but also creates challenges such as poverty, inequality and resource strain. Going forward, sustainable development and strong social protection will be key to underpinning India’s economic stability and growth.
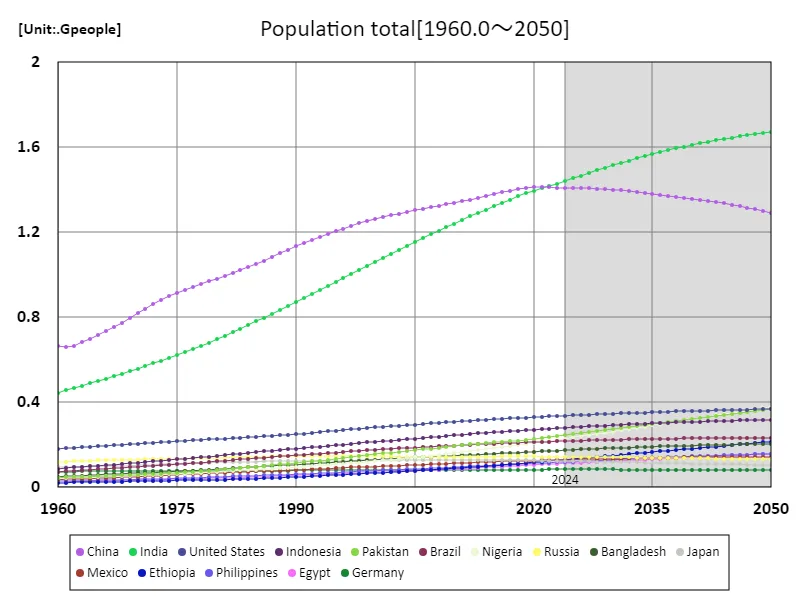

The maximum is the latest one, 1.67Gpeople of India
Total population (worldwide, latest year)
By 2050, India is projected to have the world’s largest population, reaching 1.67 billion. This will contribute to India’s increasing overall economic clout. The average population is 47.7 million, while the world population has reached 9.3 billion and is showing a rapid growth trend. Data from the past few decades has shown rapid population growth in developing countries in Asia and Africa, while developed countries have seen relatively stable or declining populations. India’s rapid growth has brought about an increase in the labor force and an expansion of the consumer market, but it has also highlighted the challenges of straining social infrastructure and resources. Furthermore, an increase in average population is driving social changes such as urbanization and widening regional disparities, making sustainable development and inclusive economic policies more important.
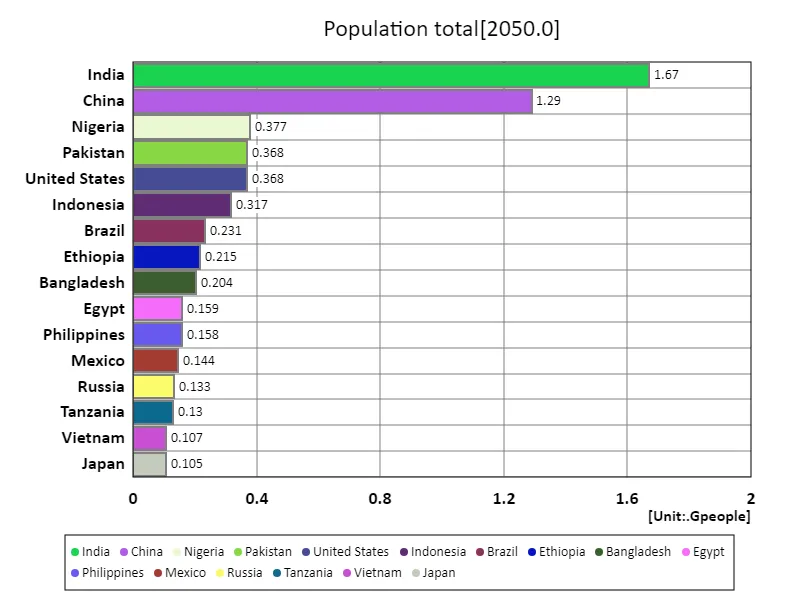

The maximum is 1.67Gpeople of India, the average is 47.7Mpeople, and the total is 9.21Gpeople
Total population (region, latest year)
By 2050, South Asia is expected to have the world’s largest population, reaching 2.38 billion people. This reflects the rapid population growth in the South Asian region. The world’s total population will reach 12.6 billion, with an average population of 840 million, a significant increase compared to previous decades. In particular, the Asian region is the centre of population growth, with countries such as India, Bangladesh and Pakistan being major contributors. While this has expanded the region’s labor and consumer markets and become a driving force for economic growth, it has also exacerbated issues such as infrastructure development, resource management, and environmental protection. A rapidly growing population may also increase pressure on social services such as education and health care, widening economic disparities between regions.
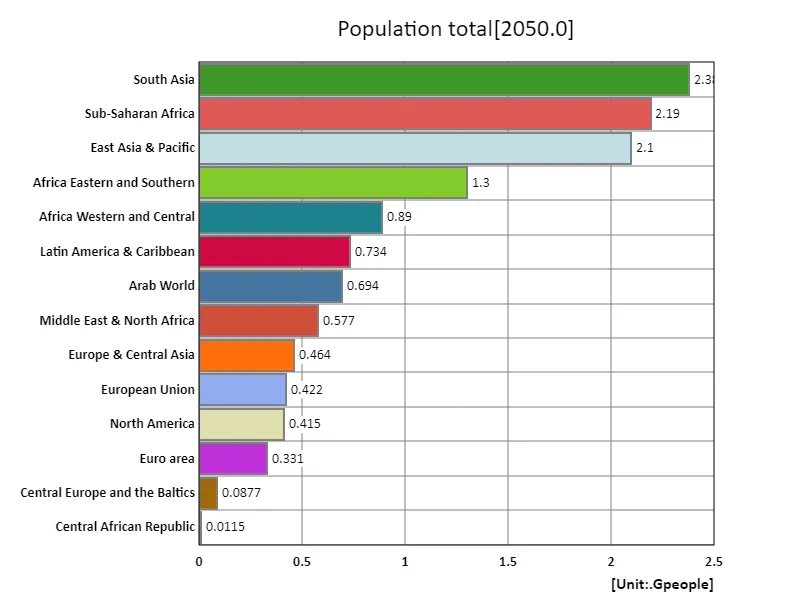

The maximum is 2.38Gpeople of South Asia, the average is 840Mpeople, and the total is 12.6Gpeople



Comments