Abstract
In recent years, Iran has experienced fluctuating GDP per capita trends, influenced by economic sanctions, oil exports, and domestic policies. Despite challenges, including inflation and a devalued currency, its GDP per capita (LCU) has shown resilience, reaching 1.63 GLCU in 2023. The country’s economy remains heavily reliant on oil, but there are ongoing efforts to diversify. Over time, these dynamics reflect both the impact of international relations and the internal structural changes in Iran’s economy, shaping its relatively high GDP per capita in the region.
GDP per capita (LCU)
Iran’s GDP per capita (LCU) has evolved through significant fluctuations, with its peak in 2023 reaching 1.63 GLCU, marking a return to its highest level since records began in 1960. This growth reflects a period of economic recovery, despite challenges like sanctions and inflation. Historically, Iran’s economy has been highly dependent on oil exports, which have driven fluctuations in GDP growth. The 2023 milestone highlights the impact of both domestic reforms and international economic pressures, with Iran at 100% of its historical peak, signaling resilience amid adversity.
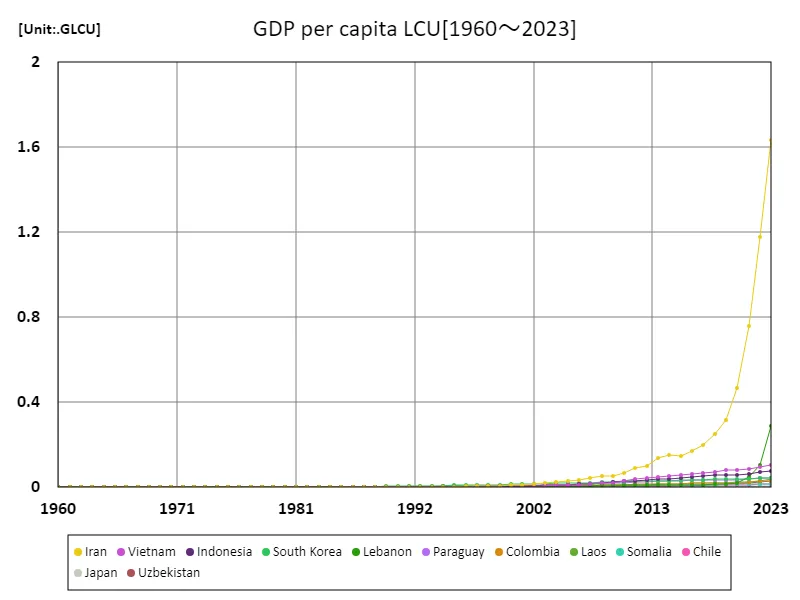

The maximum is the latest one, 1.63GLCU of Iran
GDP per capita (LCU) (world countries)
GDP per capita (LCU) in the world economy plays an important role as an individual assessment of countries’ economic activity. Looking at data from 1960 to 2023, many countries have experienced economic development and their GDP per capita is on the rise. Especially in emerging market economies and some developing countries, economic growth is remarkable and GDP per capita is soaring. On the other hand, developed countries that have enjoyed economic stability over the long term have maintained high levels of GDP per capita. However, various factors influence each country’s economic growth, with political stability, the availability of natural resources, and the progress of technological innovation being important factors. In the case of Iran, its abundant oil resources contribute significantly to its GDP per capita, recording great results as an indicator of economic development. However, the country is also affected by political instability and international sanctions, and challenges remain for sustainable growth. In the future, economic diversification and improved international relations will become important issues, which are expected to contribute to the growth and stability of the global economy, including Iran’s.
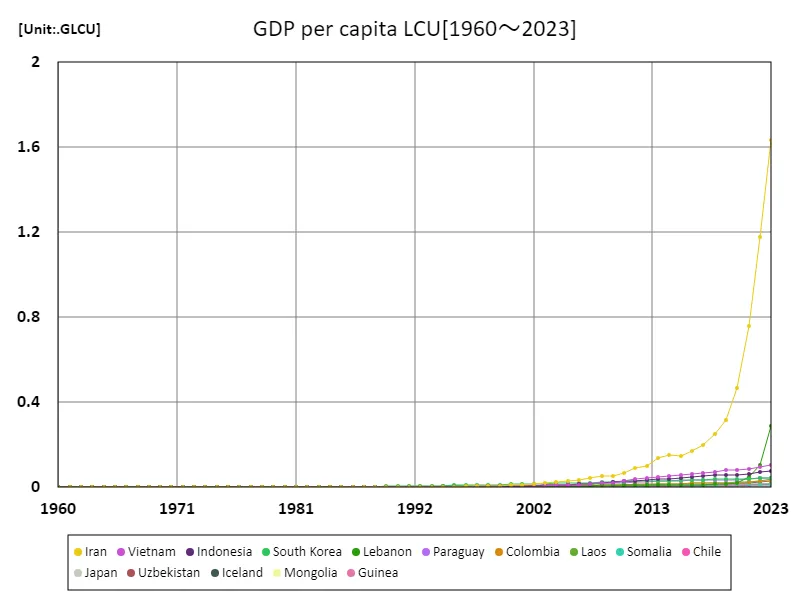

The maximum is the latest one, 1.63GLCU of Iran
GDP per capita (LCU) (world countries, latest year)
Global GDP per capita (LCU) data reveals patterns of economic inequality and growth. Iran’s overall maximum of 1.63 glcu for 2023 represents a temporary peak for its economy, but it also means that the figure will depend heavily on domestic resources and the political situation. On the other hand, the overall average of 13.7 mlcu represents the average level of economic activity across the global economy. The differences are due to the stage of economic development, industry diversity and the spread of technology, and also suggest that the average is rising as emerging and developing countries grow. The total value of 2.48 glcu represents the size of the world’s economy as a whole, reflecting the contributions of large nations and economic blocs. Going forward, the global economy will face challenges including the sustainability of economic growth, reducing economic disparities, and promoting technological innovation.
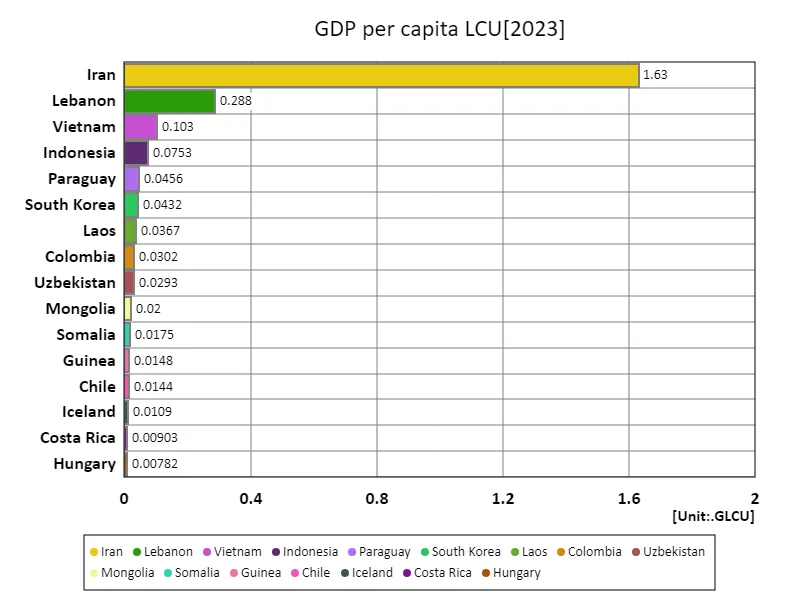

The maximum is 1.63GLCU of Iran, the average is 13.8MLCU, and the total is 2.48GLCU



Comments