Abstract
The annual growth rate of the manufacturing sector is a key indicator of a country’s economic health and industrial development. Iraq’s growth rate of 10.9% in 2023 means that the country’s manufacturing industry is developing rapidly. Iraq’s high growth rate can be attributed to post-war reconstruction and stabilization, as well as new economic policies and increased investment. On the other hand, historical trends show that countries with high growth rates are often driven by resource development and active government support. While manufacturing growth is typically an important driver of overall economic growth, whether high growth rates are sustainable depends on factors such as infrastructure development, political stability, and inflows of foreign direct investment. In Iraq’s case, improvements in these factors appear to have accelerated manufacturing growth, but its sustainability and fundamentals also need to be assessed when comparing growth rates with those of other countries.
Manufacturing, annual growth rate
The annual growth rate of the agricultural, forestry and fishery manufacturing sector is an indicator that reflects a country’s economic development, policies and resource utilization. Looking at data from 1961 to 2023, the unusually high growth rate of 913% recorded by Iraq in 1980 may indicate unique economic conditions or statistical anomalies during that period. Iraq’s rapid growth was likely influenced by certain policies, industrial investment, and external support at the time. However, the current annual growth rate of Iraq’s agriculture, forestry and fishing manufacturing sector is just 1.19 percent, a significant decline compared to past peaks. This change suggests that development in the agriculture, forestry and fisheries sectors is stagnating due to factors such as war, political instability and the deterioration of infrastructure. In many countries, growth rates of agriculture, forestry and fisheries are often unstable and are particularly sensitive to changes in resources and policies. Overall, the growth rates of the agriculture, forestry and fisheries sectors are highly dependent on fluctuations in the overall economy, agricultural policies and trends in international markets, and countries that achieve high growth rates often find it difficult to maintain that growth in the long term. The change in Iraq’s past and present growth rates speaks to the country’s economic challenges and the impact of external factors.
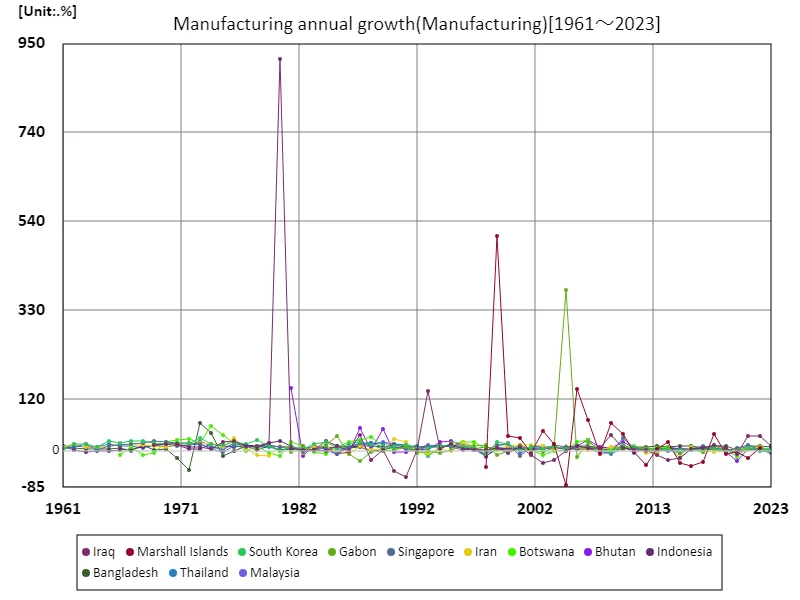

The maximum is 913%[1980] of Iraq, and the current value is about 1.19%
Manufacturing, annual growth rate (worldwide)
The annual growth rate of the manufacturing industry is an important indicator of a country’s industrial development and economic performance. Looking at data from 1961 to 2023, the high growth rate recorded by Iraq in 1980, 913%, stands out. This peak can be attributed to the rapid growth of Iraq’s oil industry at the time, reflecting large-scale investment and successful policies. However, Iraq’s current manufacturing growth rate has fallen to 1.19%, a significant drop from its peak. This change can be attributed to war, political turmoil, and a lack of economic diversification. In other countries too, the growth rate of manufacturing is heavily influenced by domestic and international economic factors and industrial policies, and long-term sustainability is a question. Overall, the growth rate of the manufacturing industry depends on factors such as a country’s industrial policy, the investment environment, and progress in technological innovation. Whether high growth rates can be sustained depends on economic diversification, market expansion, and improved quality of human resources. The case of Iraq illustrates temporary growth and the challenges that followed, making it an important example that can provide insight into the industrial policies and development strategies of other countries.
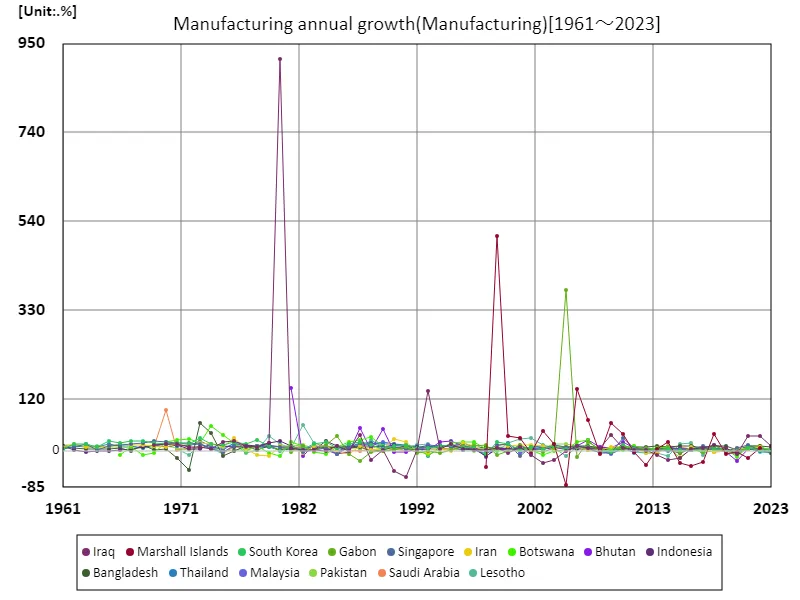

The maximum is 913%[1980] of Iraq, and the current value is about 1.19%
Manufacturing, annual growth rate (world countries, latest year)
Annual manufacturing growth is a key indicator of a country’s industrial strength and economic health. Data for 2023 shows that Slovakia will record the highest growth rate of 19.3%, while the overall average is 1.04%. Slovakia’s strong growth reflects the country’s active efforts in industrial diversification and technological innovation. However, the relatively low overall growth rate of 1.04% indicates the challenges facing the manufacturing industry and the impact of the domestic and international economic environment. The total manufacturing growth rate of 131% illustrates the evolution and transformation of the industry over the past few decades. As many countries industrialize and enter a mature stage, their growth rates experience certain cyclical fluctuations. The growth rate of the manufacturing industry is also influenced by national policies and fluctuations in market demand, with technological advances and the development of international trade being particularly important factors. Looking ahead, investment in innovation and the promotion of green manufacturing processes are needed to foster sustainable growth. Furthermore, education and skills development are becoming increasingly important in order to increase international competitiveness. Changes in the growth rate of the manufacturing industry will be a barometer of each country’s economic strategy and its results, and will be a key factor in sustainable development.
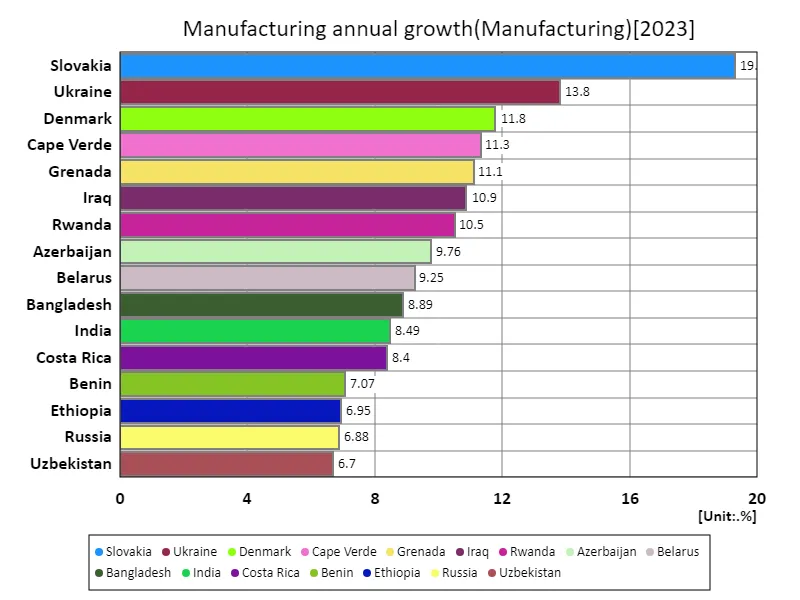

The maximum is 19.3% of Slovakia, the average is 981m%, and the total is 123%
Manufacturing, annual growth rate (region, latest year)
Data on agriculture, forestry and fisheries manufacturing for 2023 shows South Asia posting the highest annual growth rate at 6.95%. This demonstrates that South Asia is actively working to modernize and streamline its agriculture, forestry and fisheries sectors. South Asia is seeing increased technological innovation and investment to meet the growing demand for food as populations and economies grow. An overall average growth rate of 166m% does not generally indicate very high growth and the data should be interpreted with caution. On the other hand, the total growth rate of 1.82% indicates that the overall growth of the agriculture, forestry and fisheries sectors is slow. This growth rate could reflect industry maturity, market stabilization, and the impact of external factors such as weather and natural disasters. Historically, agriculture, forestry and fisheries are sectors where stability is required in many countries, and while emerging and developing countries have experienced rapid growth, growth has tended to slow in mature economies. Additionally, climate change and the promotion of sustainable agriculture will have a major impact on future growth. Overall, the agricultural, forestry and fisheries manufacturing sector is characterised by a wide range of growth due to regional differences and external factors.
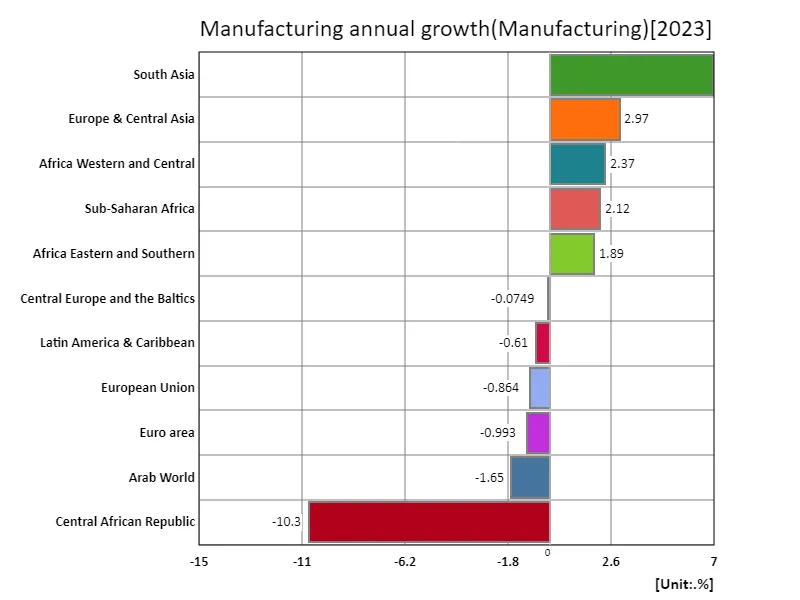

The maximum is 6.95% of South Asia, the average is 166m%, and the total is 1.82%



Comments