Abstract
Based on June 2024 exchange rate (new lcu/US dollar, period average) data, Lebanon’s 89.5klcu is particularly eye-catching. Such a high exchange rate suggests that Lebanon’s economy is facing severe inflation and a rapid devaluation of the currency. Over the past few years, Lebanon has been hit by an economic crisis, with political instability and a collapsing financial system taking its toll. Similar trends are seen in other countries, especially in the Middle East and Africa, where political factors and social unrest often have a negative impact on currency values. Insufficient external capital inflows and international investment also hinder the stability of the currency. In contrast, countries with relatively stable currencies tend to foster economic growth and foreign direct investment, which in turn leads to stable exchange rates. Overall, exchange rate fluctuations are an important indicator that reflects a country’s economic situation, and the case of Lebanon in particular shows the importance of economic policies and international influences. Political stability and sound monetary policies are essential for future economic recovery.
Exchange rate (new lcu/US dollar, period average)
Looking at monthly exchange rate data from 1987 to June 2024, the figures reflect the economic turmoil of the time, particularly Angola’s record of 2.18 mlcu in June 1995. This peak marked the rapid inflation caused by civil war and political instability, which resulted in Angolan currency subsequently losing 39.6m% of its value. Over the past few decades, in many developing countries, exchange rate fluctuations have reflected the health of their economies and the effectiveness of their policies. Exchange rate volatility is particularly prevalent in countries experiencing civil war, economic sanctions, and high resource dependency. Countries that depend on oil revenues, like Angola, are sensitive to fluctuations in oil prices and are vulnerable to swings in the international market. On the other hand, countries with stable political environments and diversified economic bases tend to have relatively stable exchange rates and achieve sustainable growth. Against this backdrop, we can see that exchange rates are more than just numbers; they are an important indicator of a country’s economic health. Future economic policies will need to aim for a stable currency and sustainable growth.
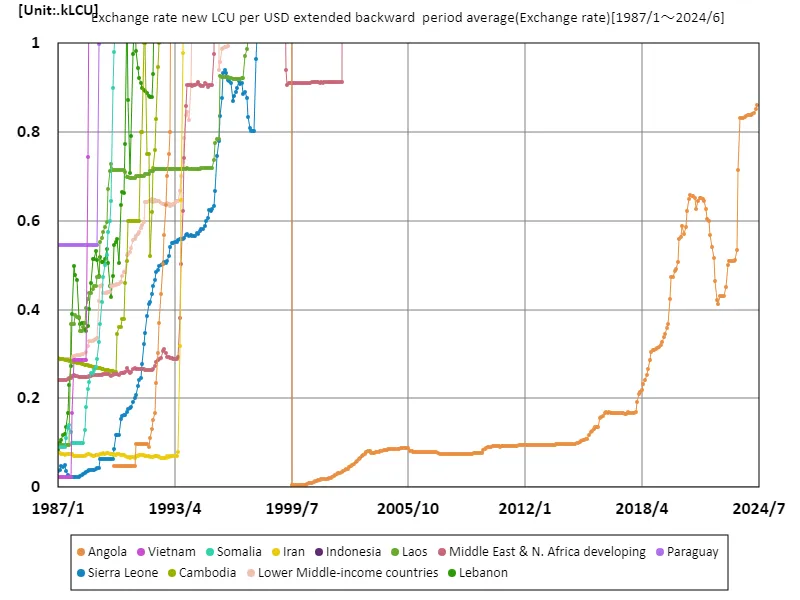

The maximum is 2.18MLCU[1995年6月] of Angola, and the current value is about 39.6m%
Exchange rates (new lcu/US dollar, period average) (countries around the world)
Looking at data on exchange rates (new lcu/US dollar, period average) from 1987 to June 2024, the 2.18 mlcu recorded by Angola in June 1995 is particularly noteworthy. This figure reflects the fact that Angola was facing severe inflation due to civil war and economic instability. Since then, Angolan currency is now worth 39.6m% less than its peak, suggesting the economy has a long way to go before it recovers. Looking at the trends in this data, we can see that developing countries experience particularly high exchange rate volatility. Currency stability is often threatened, especially in countries with political instability, civil war, or a high dependency on resources. Countries that depend on oil resources, like Angola, are vulnerable to international market influences and are at increased risk of sudden fluctuations in exchange rates. Conversely, countries with stable political environments tend to enjoy relatively stable exchange rates due to diversified economic bases and prudent monetary policies. Against this backdrop, the exchange rate is an important indicator of a country’s economic health. In order to achieve sustainable economic growth going forward, stable monetary policies as well as the flexibility to adapt to changes in the international economic environment will be required.
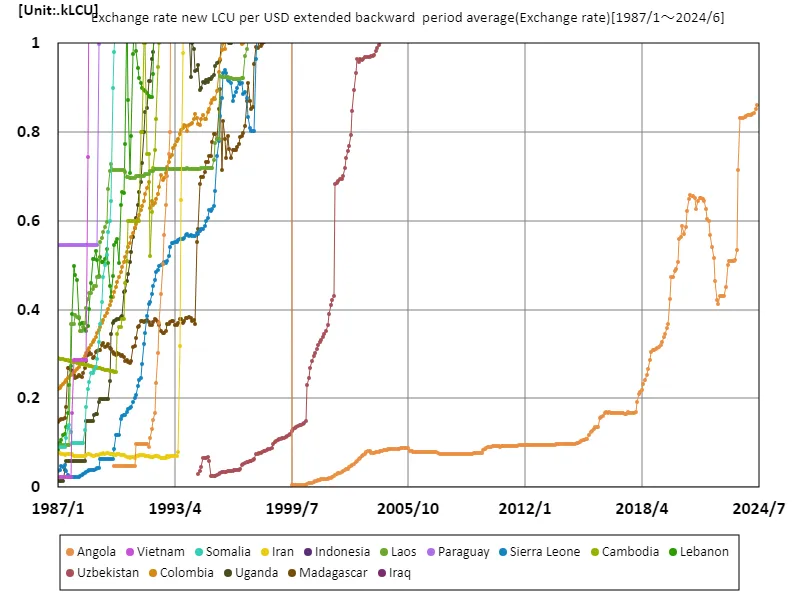

The maximum is 2.18MLCU[1995年6月] of Angola, and the current value is about 39.6m%
Exchange rate (new lcu/US dollar, period average) (by income, latest year)
According to July 2023 exchange rate (new lcu/US dollar, period average) data, the maximum value for upper-middle-income countries is 831 lcu, the average is 447 lcu, and the total is 893 lcu. These figures are important indicators of the stability of middle-income countries’ currencies and their influence in international markets. High exchange rates in upper-middle-income countries reflect stronger economic growth and attracting international investment. The high value of 831 lcu indicates that these countries have stable economic foundations and growth prospects. On the other hand, the average value of 447lcu indicates that there are differences in currency values, and that differences in economic situations and policies of each country affect exchange rates. The total of 893 lcu represents countries that are particularly economically unstable and vulnerable to external factors. In these countries, political turmoil and inflation often have a negative impact on exchange rates, calling for improved economic policies. Overall, exchange rates are an important indicator of a country’s economic performance, and countries with stable currencies are in a better position to attract investment and expand trade. Future economic policy needs a strategy aimed at sustainable growth and monetary stability.
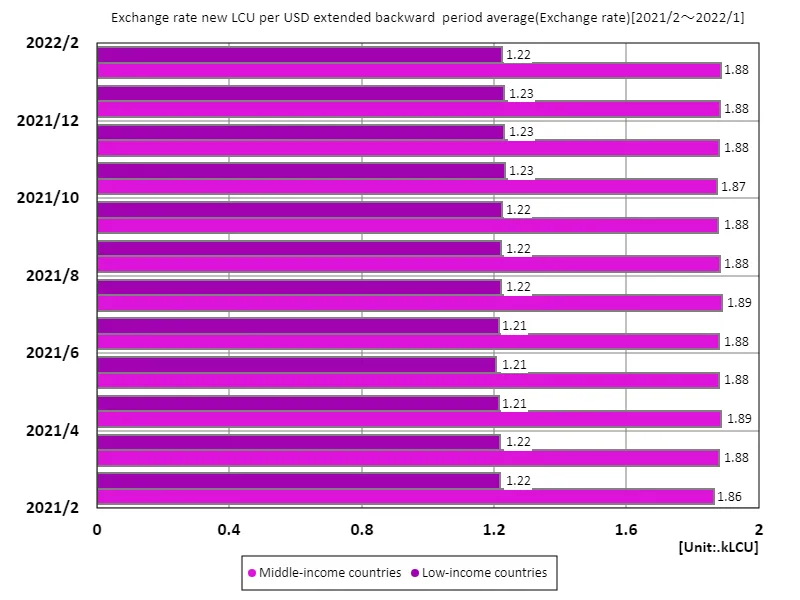

The maximum is 1.89kLCU[2021年7月] of Middle-income countries, and the current value is about 99.8%



Comments