- Abstract
- Customs clearance of imported goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted))
- Customs clearance of imported goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (countries around the world)
- Customs clearance of imported goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (Worldwide, latest year)
- Customs clearance of imported goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (region, latest year)
- Reference
Abstract
The customs clearance value of imported goods in April 2024 reached USD 3.23 trillion, suggesting a recovery in the global economy. The figures reflect increased trade activity among countries as they recover from the impacts of COVID-19. In particular, demand from the Asia-Pacific region and North America is increasing, leading to increased imports of electronic equipment and raw materials. Looking back at the past few years, fluctuations in global supply chains and geopolitical tensions have impacted trade, but data for 2023-2024 shows that these obstacles have been overcome and collaboration between countries has strengthened. Additionally, due to environmental concerns, imports of sustainable goods and services are also on the rise, and this is expected to be a future trend to watch. However, inflationary pressures and supply shortages remain concerns, which could affect import costs and commodity prices. Overall, the 2024 import clearance data is a key indicator that the global economy is entering a new phase of growth.
Customs clearance of imported goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted))
Customs data on imported goods from 1990 to April 2024 provides a stark picture of the changes in the global economy. Notably, the peak of USD 3.65 trillion recorded in June 2022 reflected a rapid recovery in demand following the pandemic, although the current figure is only 88.5% of that since then. This suggests that supply chain disruptions, geopolitical risks and inflationary pressures are all playing a role. From the 1990s to the early 2000s, trade expanded as globalization progressed, and many countries achieved economic growth. However, trade has seen frequent fluctuations due to the 2008 financial crisis and the recent pandemic. In particular, in 2020, imports temporarily fell sharply due to the impact of COVID-19, and then recovered rapidly, but growth has slowed since 2023 due to supply instability and rising energy prices. Currently, countries are stepping up efforts towards sustainable trade, with greater attention to the environment and digitalisation. These changes will have a major impact on future trade trends.
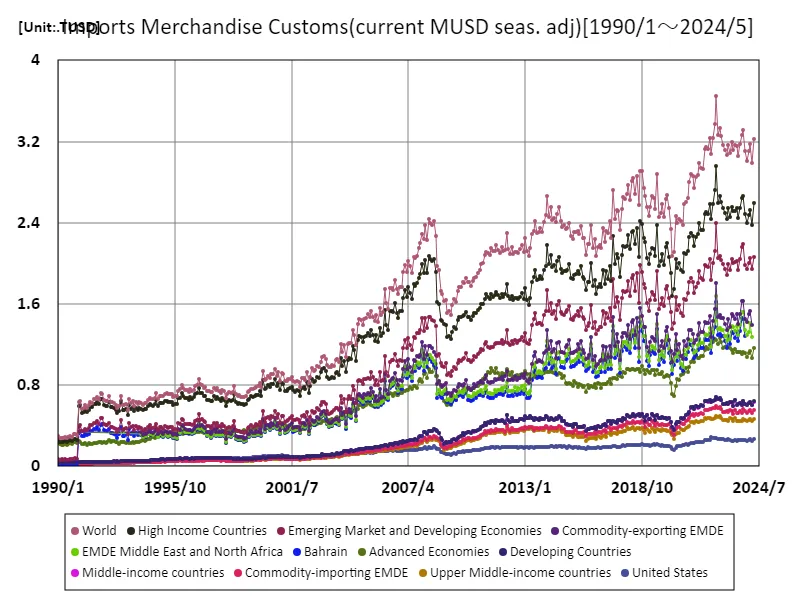

The maximum is 3.65TUSD[2022年6月] of World, and the current value is about 88.5%
Customs clearance of imported goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (countries around the world)
Bahrain’s customs data on imported goods from 1990 to May 2024 highlights the evolution of its economy and the characteristics of its trade. Notably, while the USD 1.62 trillion recorded in June 2022 represents rapid growth in the Bahraini economy, the fact that the current figure is only 79.1% of that figure indicates several factors are at work. Bahrain has been diversifying its economy from its past reliance on the oil industry, and is seeing growth in financial services and tourism. In recent years in particular, the city has strengthened its position as an international trading hub and has seen a diversification of imported goods. However, import activity is slowing due to fluctuations in energy prices from 2023 onwards and disruptions to global supply chains. Additionally, regional political conditions and economic policies are also important factors. Bahrain aims to be a stable trading nation in the Middle East, but is sensitive to changes in the external environment, and these factors directly lead to fluctuations in import customs clearance. Going forward, strategies for sustainable economic growth will be required, and new prospects for trade based on environmental considerations and technological innovation are anticipated.
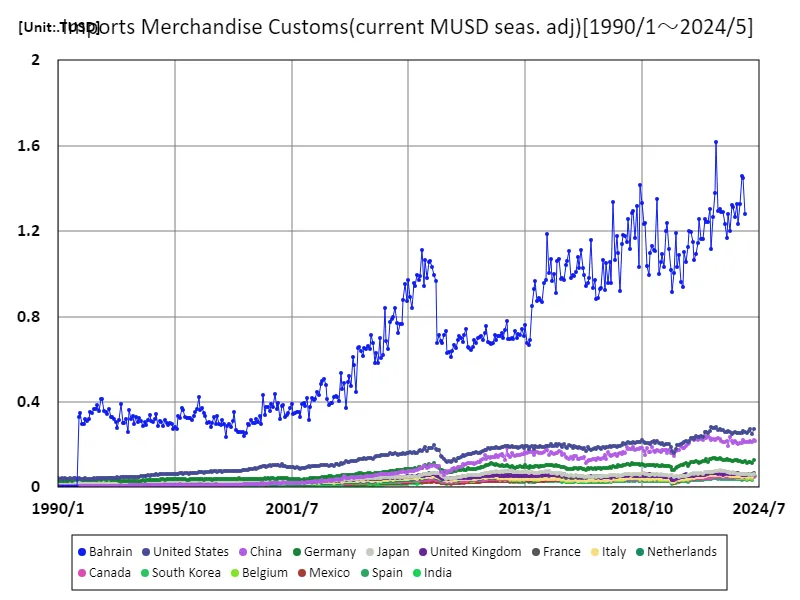

The maximum is 1.62TUSD[2022年6月] of Bahrain, and the current value is about 79.1%
Customs clearance of imported goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (Worldwide, latest year)
Customs clearance data for imported goods in May 2023 is an important indicator for understanding the current state of the global economy. Imports from high-income countries reached USD 2.67 trillion, with an overall total of USD 3.95 trillion and an average of USD 1.23 trillion, indicating that economic activity in developed countries remains strong. This situation is likely due to the post-pandemic recovery and a rebound in consumption. High-income countries are importing increasing amounts of goods, particularly technology-related goods and energy resources, and are becoming more dependent on global supply chains. Meanwhile, low-income countries have seen uneven economic growth and a tendency to constrain trade activity. Additionally, inflationary pressures and geopolitical risks are affecting trade, with fluctuations in energy prices in particular directly affecting import costs. Looking back at the data to date, while economic globalization continues to progress, the impact of each country’s policies and international situations on trade cannot be ignored. As sustainable trade becomes more important in the future, countries will be required to take environmental concerns into consideration and make efforts to strengthen supply chains. This is expected to lead to future trade stability and growth.
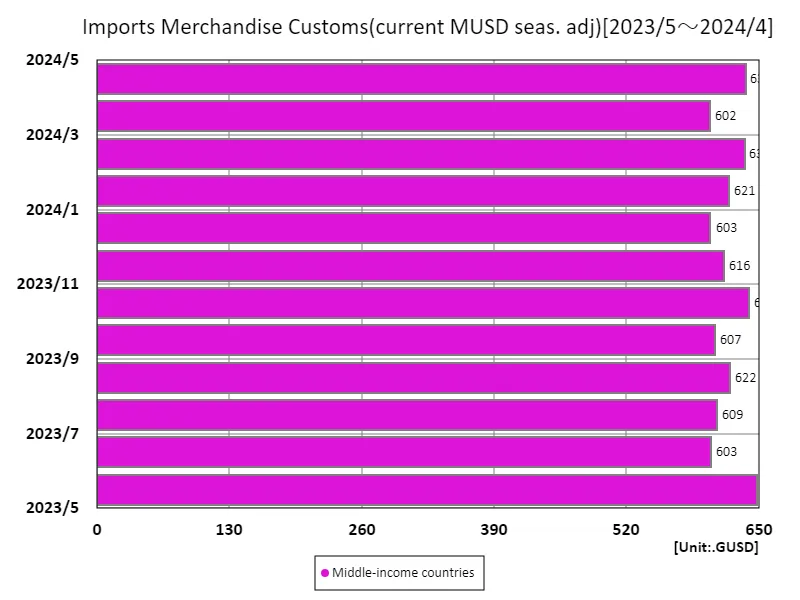

The maximum is 649GUSD[2023年5月] of Middle-income countries, and the current value is about 98.2%
Customs clearance of imported goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (region, latest year)
Customs clearance data for imported goods for April 2024 is an important indicator for understanding the dynamics of the global economy. Imports from high-income countries reached USD 2.59 trillion, with an overall total of USD 3.7 trillion and an average of USD 1.23 trillion, highlighting the strength of consumption and trade in developed countries. In particular, there is growing demand for technology products and energy resources, which is driving an increase in the import bill. Looking back over the past few years, we can see that economies around the world have revitalized following the post-pandemic recovery. However, geopolitical risks and the effects of inflation cannot be ignored, and fluctuations in energy prices in particular are having a major impact on trade. High-income countries are exploring new trade partnerships to maintain stable supply chains. Meanwhile, economic growth remains uneven in low-income countries, often limiting trade activity. In these circumstances, sustainable trade is becoming increasingly important, with greater consideration given to the environment and stronger supply chains required. Going forward, each country will need to address these challenges while aiming for trade stability and growth.

The maximum is 637GUSD of Middle-income countries, the average is 637GUSD, and the total is 637GUSD



Comments