Abstract
According to data from May 2024, the unemployment rate in Poland is 5.1%, which is a relatively high figure. Poland has experienced strong economic growth over the past few years, but challenges remain in the labour market. In particular, the unemployment rate among young people is high, and a mismatch between education and employment is said to be one of the causes. Regional economic disparities also have an impact, with large differences in employment opportunities between urban and rural areas. Furthermore, as a member of the EU, Poland has strengthened economic ties with other European countries. While this has encouraged the inflow of foreign capital, it has also made it easier for fluctuations in the global economic environment to affect the domestic employment situation. For example, fluctuations in energy prices and supply chain issues could hurt certain industries. Overall, Poland’s unemployment rate shows different trends across regions and age groups, calling for greater labor market flexibility and stronger vocational training programs. It is expected that such measures will lead to a decline in unemployment and further stability of the economy.
Unemployment rate (%)
According to data from 1990 to May 2024, the unemployment rate in the Republic of Macedonia reached an extremely high level of 38.4% in January 2005. This peak is likely the result of structural changes in the economy and political instability. Macedonia’s economy has since gradually recovered, and unemployment is currently 33.8% lower than its peak, but it remains high. During this period, the Republic of Macedonia implemented economic reforms, placing particular emphasis on attracting foreign capital and promoting the manufacturing industry. This has resulted in an increase in employment opportunities and the unemployment rate is showing signs of improvement. However, regional disparities and youth unemployment remain problems, and employment opportunities are particularly limited in rural areas. Global economic fluctuations and the financial crisis have also affected the employment situation in Macedonia. Instability in the global economic environment can also put a brake on job creation in certain industries. Looking ahead, promoting sustainable economic growth and improving education and vocational training will be key to further reducing unemployment.
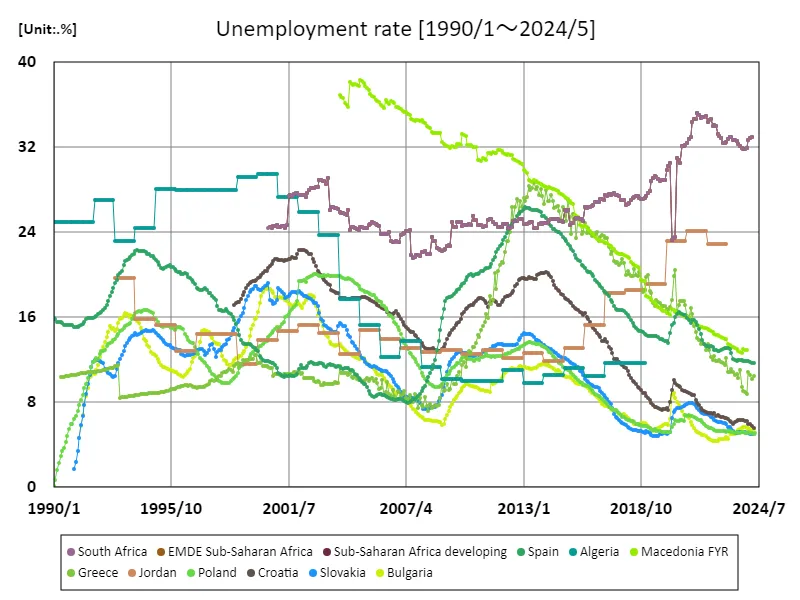

The maximum is 38.4%[2005年1月] of Macedonia FYR, and the current value is about 33.8%
Unemployment rate (%) (worldwide)
According to data from 1990 to May 2024, South Africa’s unemployment rate reached a very high level of 35.2% in July 2021. This peak is said to be the result of a combination of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic and structural problems in the economy. In particular, long-term stagnation in economic growth, the gap between rich and poor, and deficiencies in the education system are factors that are pushing up the unemployment rate. In South Africa, youth unemployment is particularly high, and barriers to entry into the job market are considered an issue. Although the government has introduced various job creation programs, challenges remain in terms of their effectiveness. In addition, the South African economy is dependent on certain industries such as mining and agriculture, and if these industries suffer a downturn, this will have a direct impact on the employment situation. In recent years, there has been growth in the digital economy and the service industry, but it is unclear how much this will contribute to improving the overall unemployment rate. Improving education and skills, especially vocational training for young people, is key to achieving sustained economic growth. How future policies respond to these challenges will be key to improving the unemployment rate.
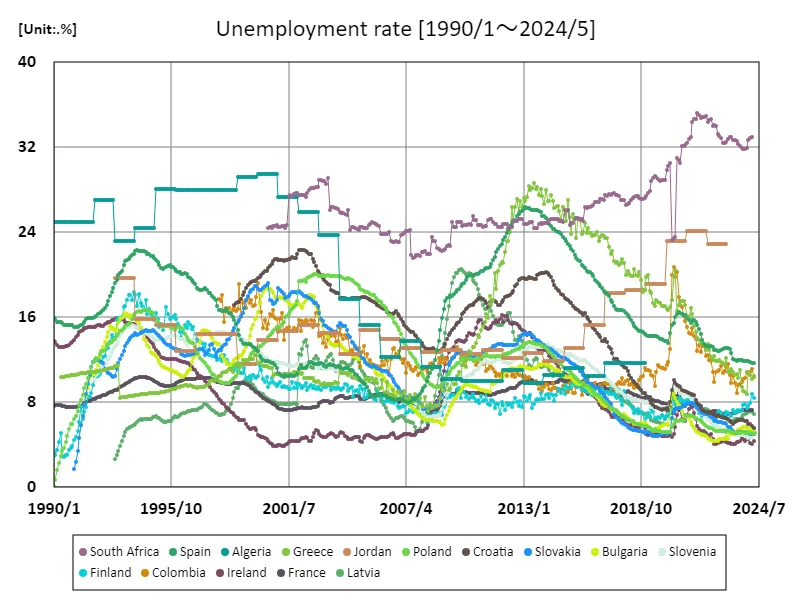

The maximum is 35.2%[2021年7月] of South Africa, and the current value is about 93.4%
Unemployment rate (%) by income, latest year
According to May 2023 data, the unemployment rate in upper-middle-income countries is 7.34%, compared with an average of 6.19% and a total of 18.6%. This figure reflects economic growth and labour market fluctuations and is an important indicator of middle-income country characteristics. While upper-middle-income countries are increasingly diversifying their economies, they remain dependent on certain industries and sectors. As a result, the economy is sensitive to global economic fluctuations and changes in supply and demand, making the unemployment rate prone to fluctuations. For example, fluctuations in manufacturing or services can have an immediate impact on employment. In addition, the unemployment rate among young people is particularly high, and the mismatch between education and the labor market is a problem. In many middle-income countries, education systems are not keeping up with industry needs, resulting in an increasing number of new graduates unable to adapt to the labour market. In addition, regional economic disparities also have an impact, with imbalances in employment opportunities between urban and rural areas. Governments need to strengthen job creation policies and vocational training programs. A comprehensive approach is required to achieve sustainable economic growth and reduce unemployment.
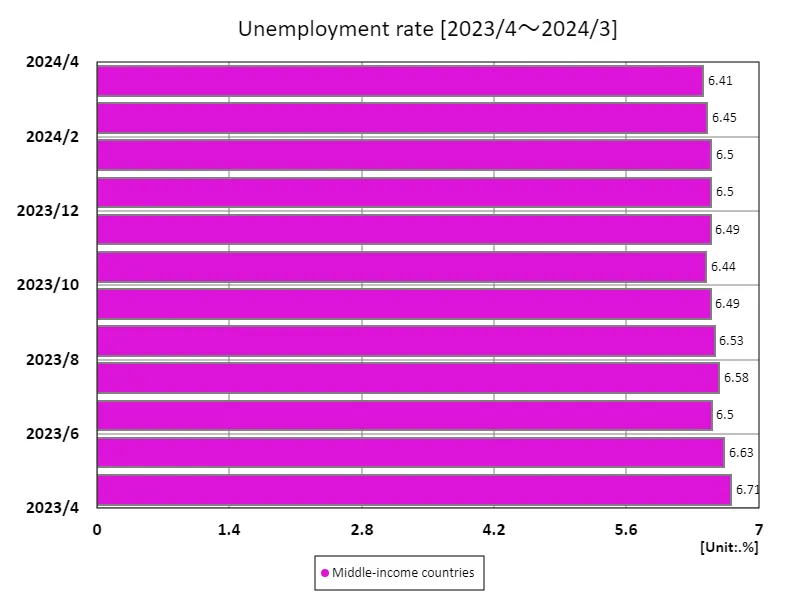

The maximum is 6.71%[2023年4月] of Middle-income countries, and the current value is about 95.6%
Unemployment rate (%) (region, latest year)
Data from April 2024 shows that the unemployment rate in upper-middle-income countries is relatively high at 6.92%, compared with an average of 5.82% and a total of 11.6%. This situation illustrates the gap that exists between economic growth and job creation. In upper-middle-income countries, although industrial structure is changing and technological innovation is progressing, a mismatch between employment supply and demand remains a problem. This is due in particular to high youth unemployment and an education system that is not keeping up with the needs of the labour market. Many new graduates lack the necessary skills, and companies continue to struggle to find suitable talent. This makes it difficult for the unemployment rate to fall. Regional economic disparities are also having an impact, with many employment opportunities in urban areas while the situation remains difficult in rural areas. For this reason, governments are being called upon to strengthen regional development and vocational training programs. In addition, the impact of fluctuations in the international economy, particularly the stock market, on the domestic employment situation cannot be ignored. A comprehensive policy approach is needed to increase economic stability and generate sustainable jobs. This is expected to improve unemployment rates and boost economic growth.

The maximum is 6.41% of Middle-income countries, the average is 6.41%, and the total is 6.41%



Comments