Abstract
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is an important indicator of a country’s economic condition and is used to grasp inflation and price trends. Data for May 2024 shows Turkey’s CPI at an exceptionally high 1,330, reflecting the effects of years of high inflation. In Turkey, the depreciation of the lira and the government’s economic policies have had an impact, with food and energy prices in particular soaring, placing a heavy burden on consumers. On the other hand, many countries around the world are struggling to contain inflation, and prices are rising even in developed countries, but extreme cases like Turkey are rare, and the CPI of other countries is relatively stable. For example, in the United States and the eurozone, central banks are trying to curb inflation by raising interest rates. Fluctuations in CPI also affect consumer purchasing power and are directly linked to economic growth. In countries where high inflation persists, it can increase economic instability and have serious effects on the investment climate and living standards. Therefore, trends in the CPI are an extremely important indicator for each country’s economic policies and market credibility.
Consumer Price Index prices (seasonally adjusted)
Long-term data on the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reveals diverse characteristics of the world’s economies. In particular, Venezuela’s staggering CPI of 864 million recorded in April 2019 is a symbol of extreme hyperinflation and indicates the severity of the country’s economic crisis. The current figure of 100% compared to the peak reflects continued economic instability and policy failures. Looking at data going back to 1987, the trends in inflation rates in developed and developing countries are strikingly different. While central bank policies typically contribute to price stability in developed countries, political factors and economic vulnerabilities play a major role in developing countries. In particular, countries such as Argentina and Turkey have also seen rapid price increases and are attempting various measures to curb inflation. In addition, fluctuations in the CPI have a direct impact on consumers’ standard of living and purchasing power, making it an important indicator in economic policy. A high inflation environment also has a negative impact on economic growth as it reduces the value of savings and discourages consumption. Therefore, trends in CPI are extremely important factors for each country’s economic strategy and the lives of its people.
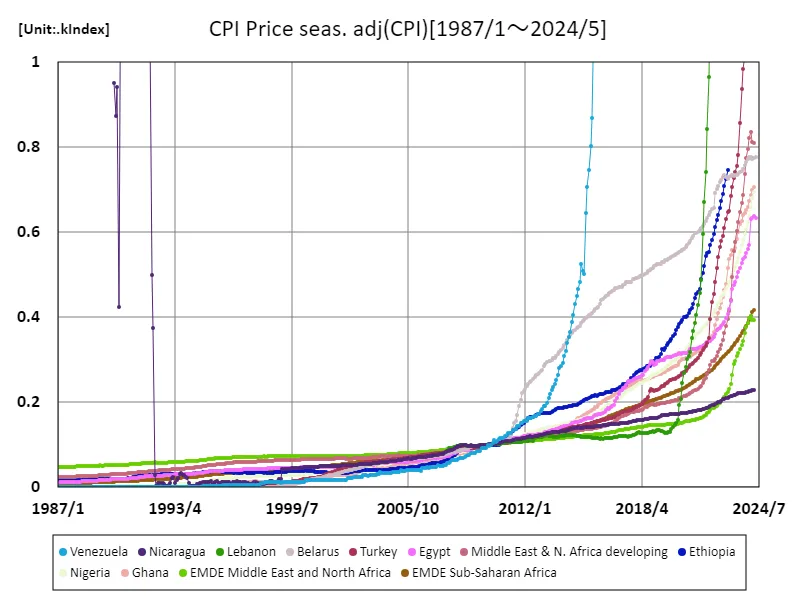

The maximum is the latest one, 864MIndex of Venezuela
Consumer Price Index prices (seasonally adjusted) (worldwide)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) data sheds light on the economic trends of each country over a long period of time, from 1987 to 2024. In particular, Venezuela’s CPI of 864 million in April 2019 represents the height of hyperinflation and illustrates the severity of its economic crisis. Venezuela’s cpi is now at 100% of its peak, symbolizing sustained inflationary pressures and economic instability. Over this period, the CPI has generally remained relatively stable in developed countries, but has shown large fluctuations in developing countries. For example, high inflation is also a problem in Argentina and Turkey, and policy responses are being attempted. Political factors and weak economic structures are the main drivers of inflation in these countries. CPI trends directly affect consumer purchasing power and living standards, so they are considered an important indicator in economic policy. Particularly in a high inflation environment, there are concerns that the real value of savings will decline and consumption activity will be suppressed, adversely affecting economic growth. Therefore, fluctuations in the CPI are an extremely important factor for each country’s economic strategy and the lives of its people.
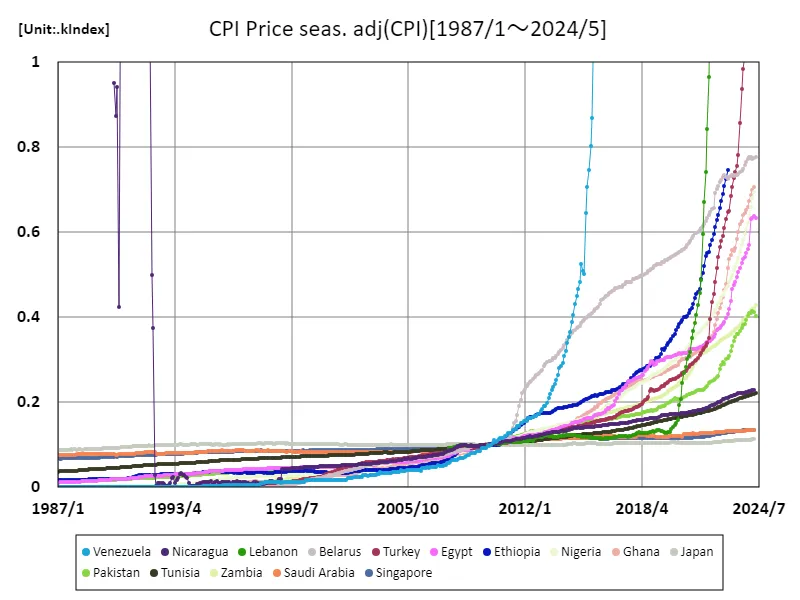

The maximum is the latest one, 864MIndex of Venezuela
Consumer Price Index prices (seasonally adjusted) (by income, latest year)
The June 2023 data for the Consumer Price Index (CPI) shows the diversity of the global economy and its fluctuations. The highest index of 234 in low-income countries reflects fragile economies, with rising food and energy prices hitting households particularly hard. Meanwhile, the average index hit 252, suggesting that an overall price increase is underway. In particular, the recent increase in cpi has been driven by supply chain disruptions, rising energy costs, and geopolitical tensions. Rising prices are also being seen in developed countries, and central banks are taking measures such as raising interest rates to curb inflation. This situation has reduced consumer purchasing power and raised concerns about economic growth. Additionally, the combined index of 1,260 indicates widespread global inflationary pressures, with the extent of their impact varying across countries and regions. Rising prices of daily necessities are having a serious impact, particularly in low-income countries, and are a factor in contributing to social instability. Therefore, trends in the CPI have become a very important indicator for each country’s economic policies and civil life.
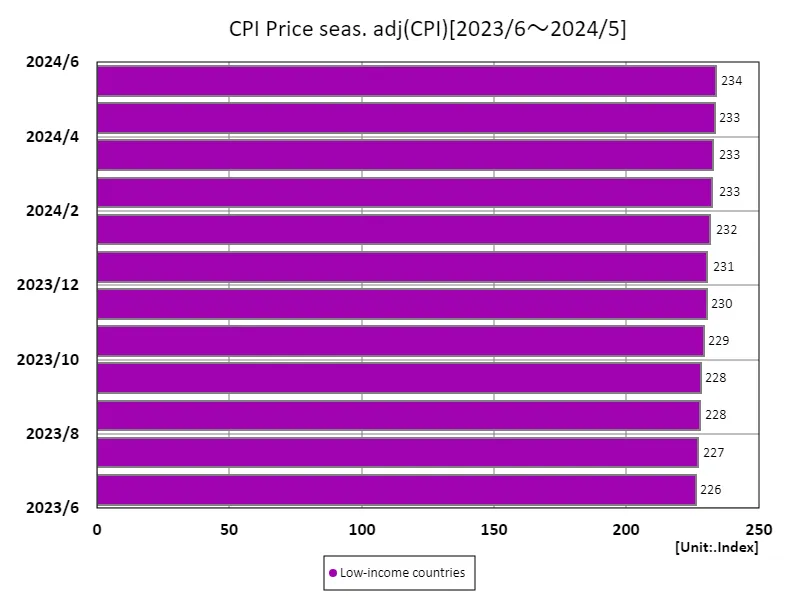

The maximum is the latest one, 234Index of Low-income countries
Consumer Price Index prices (seasonally adjusted) (by income, latest year)
The May 2024 Consumer Price Index (CPI) data reflects the current state of the economy, especially in low-income countries. The fact that the overall maximum, average and total index are all 234 indicates that these countries in particular are facing economically difficult situations. Such a high CPI is mainly due to the sharp rise in food and energy prices, putting significant pressure on household finances. In low-income countries, rising prices of basic goods often make life even harder for the poor. This could reduce consumer purchasing power and act as a drag on economic growth. Furthermore, continued inflation can increase social unrest and discontent, affecting political stability. In addition, CPI trends are also influenced by the international economic environment. For example, economic policies and market developments in developed countries can have spillover effects on prices in lower-income countries. Therefore, the CPI is an important indicator for formulating economic policy, and measures to combat inflation are urgently needed, especially in low-income countries. Given this situation, the time has come for international assistance and appropriate policies.
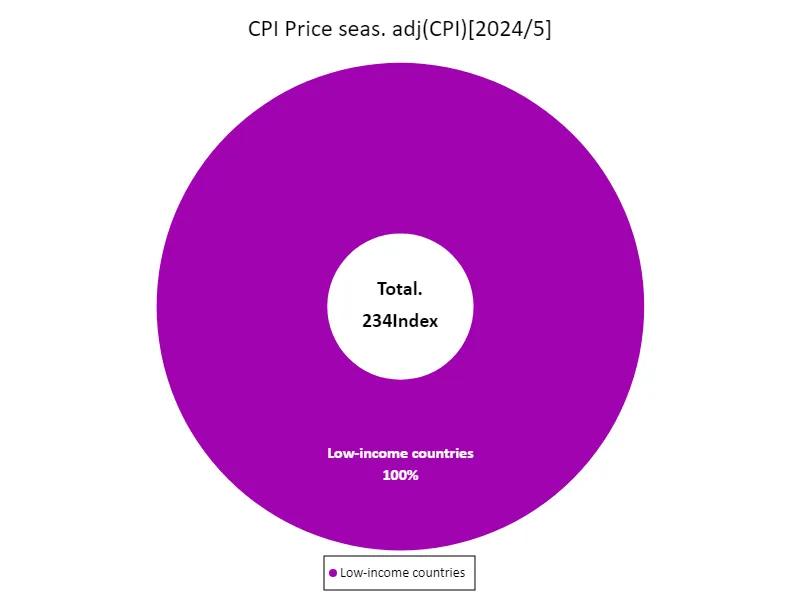

The maximum is 234Index of Low-income countries, the average is 234Index, and the total is 234Index



Comments