- Abstract
- Customs clearance of export goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted))
- Customs clearance of export goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (countries around the world)
- Customs clearance of export goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (Worldwide, latest year)
- Customs clearance of export goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (region, latest year)
- Reference
Abstract
According to data for April 2024, the customs clearance value of export goods in developing countries in East Asia and the Pacific reached 410 GUSD, a notable result. The region is characterized by rapid economic growth and a diverse industrial structure. Growth in the manufacturing and high-tech industries has been particularly notable, with China and other countries playing an important role in the global supply chain. Over the past few years, developing countries in East Asia have been taking advantage of their low-cost labor and efficient production capacity to boost their exports. This has improved Asia’s overall economic standing and made it more competitive with other regions. Furthermore, as trade agreements and economic integration progress within the region, trade liberalization is progressing and interdependence is strengthening. However, challenges remain, including geopolitical risks, environmental issues, and supply chain vulnerabilities. Given these circumstances, sustainable growth in the future will require economic diversification and the promotion of innovation. In particular, the digital economy and environmentally friendly sustainable development are likely to become important future strategies.
Customs clearance of export goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted))
Analyzing data from January 1990 to April 2024, the monthly customs clearance value of global export goods has shown large fluctuations. In particular, in June 2022, it hit an all-time high of 1.96tusd, but as of April 2024, it had fallen to approximately 1.79tusd, which is 91.4% of that level. This peak is likely the result of increased demand as the country recovers from the COVID-19 pandemic and the restructuring of supply chains. Historical trends clearly show that exports are dependent on major economies, especially China, the US and EU countries. Additionally, exports of digital and high-tech products have surged in recent years, changing the structure of the manufacturing industry. On the other hand, geopolitical risks, trade frictions, and environmental issues are factors that have an impact on exports, increasing economic uncertainty. Data from the early 2020s highlights the need for new export strategies that prioritize sustainability. International trade frameworks are also expected to continue to evolve, particularly as demand for renewable energy and green technologies grows. Taking these factors into account, strategies are needed to respond to future changes in the export market.
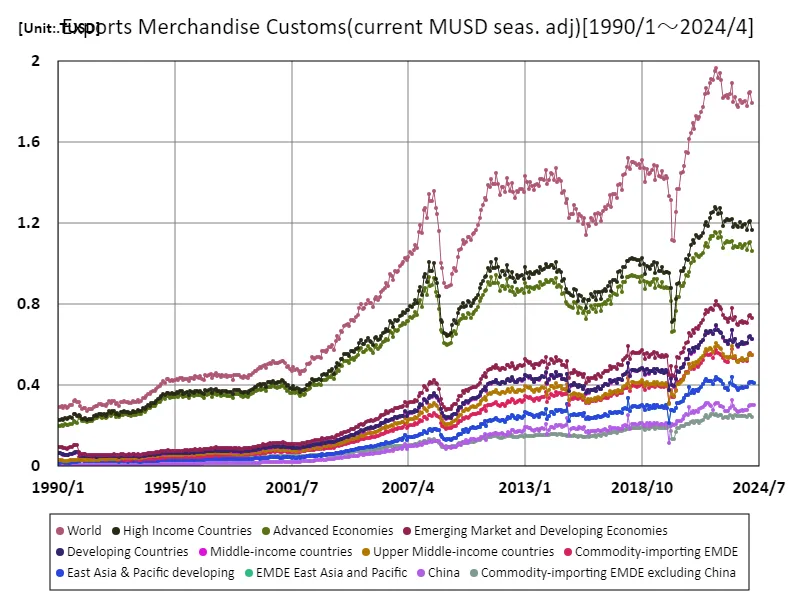

The maximum is 1.96TUSD[2022年6月] of World, and the current value is about 91.4%
Customs clearance of export goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (countries around the world)
Considering data from January 1990 to April 2024, the customs clearance value of China’s export goods is particularly noteworthy. In March 2023, it hit an all-time high of 329 gusd, but has now fallen to 91.5% of that figure. This peak is likely due to a recovery in demand following the pandemic and reorganization of global supply chains. China has a diverse range of export items, primarily from its manufacturing industry, with electronic devices, machinery and clothing being its major exports. Furthermore, rapid technological innovation and improvements in production efficiency enable us to maintain our competitiveness in the global market. However, recent geopolitical tensions and trade frictions have had an impact, increasing risks to exports. In addition, domestic and international pressures such as environmental regulations and improved working conditions also influence China’s export policy. As the country is called upon to transition to sustainable development, it needs to shift towards green technologies and renewable energy. This will change our future export strategies and create new opportunities to strengthen our position in the international market.
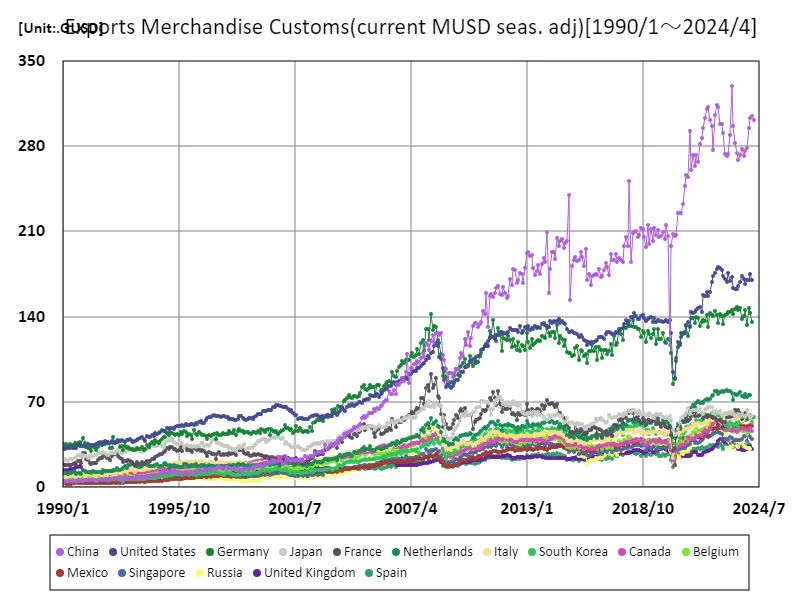

The maximum is 329GUSD[2023年3月] of China, and the current value is about 91.5%
Customs clearance of export goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (Worldwide, latest year)
According to data for April 2023, the total customs clearance value of global export goods reached 2.49 TUS, with exports from high-income countries accounting for 1.21 TUS. This high-income country’s exports account for approximately 48.6% of the world’s total, reflecting its economic stability and high technological capabilities. The average was 779 gusd, indicating that export activity overall remains strong. Historically, high-income countries have been strong primarily in manufacturing and services, with high-tech products, chemicals, and machinery and equipment being major exports. In contrast, developing countries rely mainly on resources and agricultural products and need to strengthen their manufacturing industries. Additionally, during the recovery from COVID-19, we are seeing a shift in demand, with exports of digital goods and green technology increasing. On the other hand, geopolitical risks and disruptions to supply chains will require countries to reassess their trade policies. In particular, with the demand for sustainability on the rise, the export of environmentally friendly products will become an important trend going forward. Taking these factors into account, countries need to explore strategies to enhance their competitiveness.
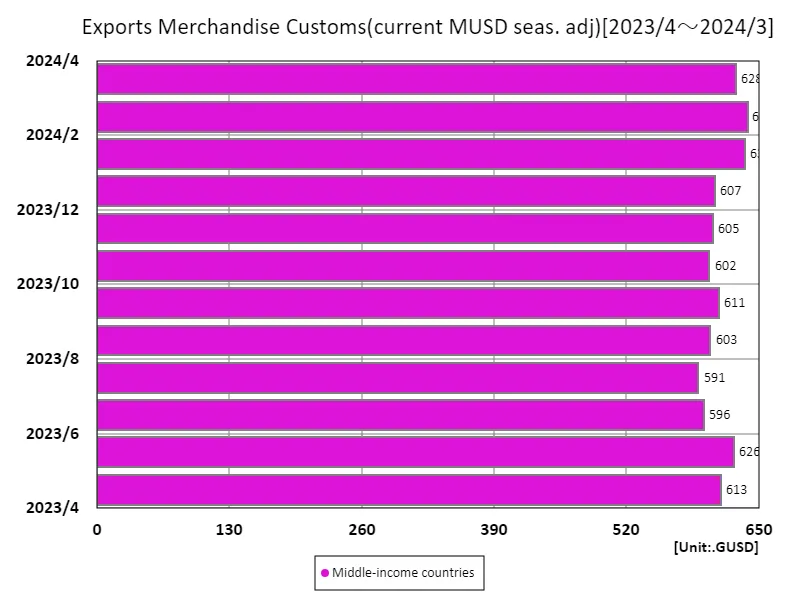

The maximum is 639GUSD[2024年2月] of Middle-income countries, and the current value is about 98.3%
Customs clearance of export goods (in current USD (seasonally adjusted)) (region, latest year)
According to data for March 2024, the total customs clearance value of global export goods reached 2.34tusd, of which high-income countries accounted for 1.16tusd. The figures show that high-income countries continue to be major players in international trade, particularly in high-tech and manufactured goods and services. The average value was 779 gusd, indicating continued strong economic activity. Historically, high-income countries have tended to expand their exports, backed by stable economic foundations and advanced technological capabilities. On the other hand, developing countries export a lot of resources and agricultural products, and there is a need to strengthen their manufacturing industries. Furthermore, as the restructuring of global supply chains progresses, economic interdependence among regions is deepening. Geopolitical tensions and changes in trade policies are also having an impact, particularly as environmental regulations and sustainability become more of a focus. This is expected to boost exports of green technology and renewable energy products. Sustainable development that responds to these trends will be key for future trade strategies.

The maximum is 628GUSD of Middle-income countries, the average is 628GUSD, and the total is 628GUSD



Comments