Abstract
Countries with a high proportion of food exports (commodity ratio) are characterized by a high degree of economic dependence, with agriculture and fisheries being major industries in particular. According to 2023 data, Belize stands out in terms of food export ratio at 95.2%, indicating that the country relies on food exports for a large part of its economy. Taking advantage of its tropical climate, Belize mainly exports agricultural products such as sugar, bananas, and citrus fruits. Looking at past trends, many of the countries with a high proportion of food exports are developing countries where agriculture is the main economic base. While these countries depend on food production and exports, they are also sensitive to fluctuations in export markets and international prices, putting their economic stability at risk. In addition, countries highly dependent on food exports often rely on limited markets and are vulnerable to fluctuations in trade policies and climate change.
Food exports (% of merchandise)
The impact of food exports (as a percentage of goods) on the economy has changed over time. Based on data from 1962 to 2023, countries with a high food export ratio usually have agriculture and fisheries as their key industries. Belize in particular recorded a peak of 136% in 1984, and has since declined to its current level of 69.9% as its economy diversifies. Throughout this period, countries with a high proportion of food exports have faced challenges in trade stability. It is vulnerable to fluctuations in market demand and climate change, which can have a significant impact on the country’s economic stability. In addition, countries with a high food export ratio are seeking to improve agricultural productivity and diversify export destinations in order to remain competitive in the international market. On the other hand, countries where the food export ratio is declining are experiencing economic diversification due to industrialization and the development of the service industry. This has improved economic stability and helped diversify trade risks. Changes in the food export ratio are an important indicator for considering the impact on each country’s economic strategy and sustainable development goals.
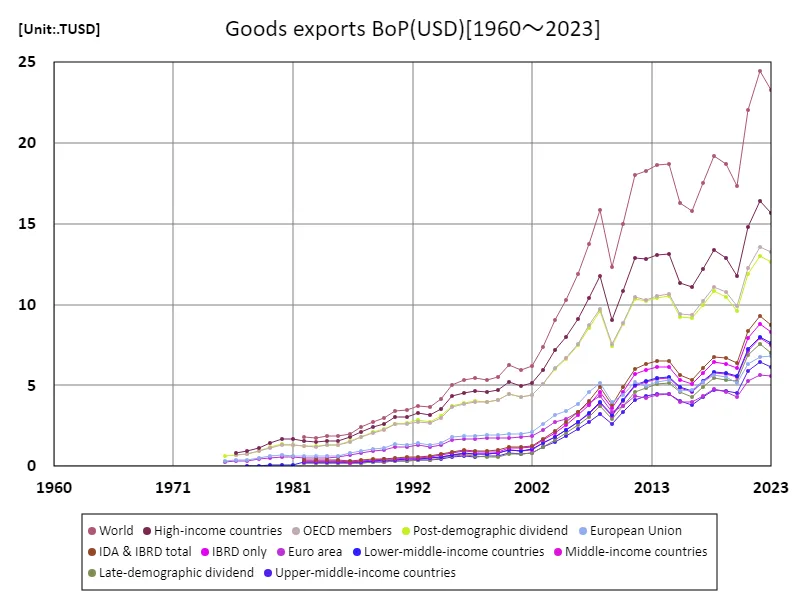

The maximum is 24.5TUSD[2022] of World, and the current value is about 95.2%
Food exports (% of merchandise) (worldwide)
Data from 1962 to 2023 shows that fluctuations in food exports (commodity ratio) reflect the economic changes in the country. In 1984, Belize’s food export ratio reached a record high of 136%, but has since declined to 69.9%. This change suggests that the country is diversifying its economy and becoming less dependent on agriculture. Over the past few decades, countries with high food export ratios have tended to be highly dependent on the agricultural sector, especially in developing countries. These countries are at risk of being sensitive to food price fluctuations and climate change, making their economic stability vulnerable. The decline in food export ratios is evidence of these countries’ industrialization and expansion of their service sectors, signaling a strategic shift towards greater economic stability. The decline in the food export ratio is also related to factors such as the diversification of export markets and the development of new industries. This helps diversify economic risks and improves trade stability. Overall, fluctuations in food export ratios reflect the changing economic structures of countries and their evolving strategies in international markets.
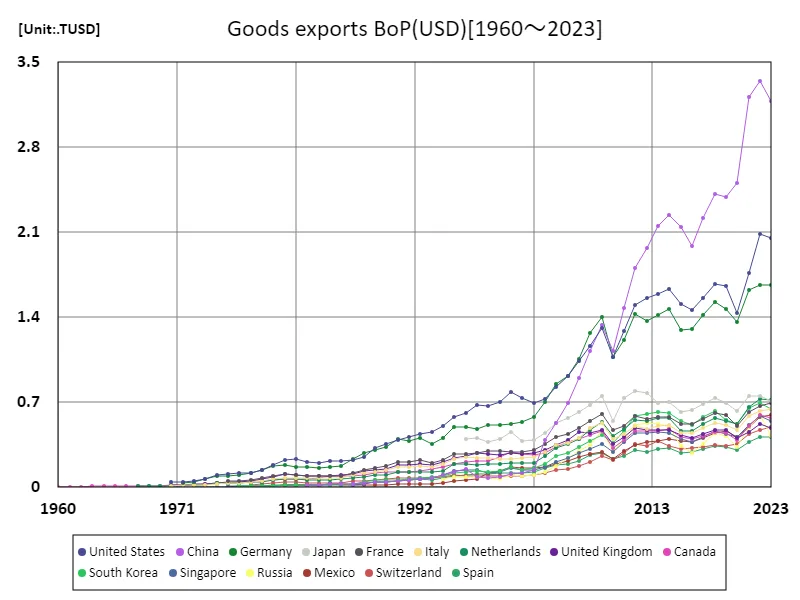

The maximum is 3.35TUSD[2022] of China, and the current value is about 95%
Food exports (% of merchandise) (worldwide, latest year)
The 2023 data on food exports (percentage of goods) shows the food dependency of countries in the global economy. Sao Tome and Principe recorded a high ratio of 98.2%, reflecting the country’s economy’s primary reliance on agriculture and fishing. On the other hand, the overall average was 23.9%, indicating the diversity of economic structures among countries. Over the past few decades, countries with a high food export ratio have typically been developing countries where agriculture and fishing, which utilize natural resources, are the main industries. This makes the country’s economy sensitive to food prices and the supply and demand balance in international markets and may be vulnerable to external economic shocks. On the other hand, countries with low food export ratios are focusing on industrialization and service sector growth and diversifying their economies. Overall, the food export ratio is an important indicator of countries’ stage of economic development and their progress towards sustainable development goals. Countries with high ratios require special attention in terms of food security and trade stability, and require diversification and improved seismic resilience in their economic policies.
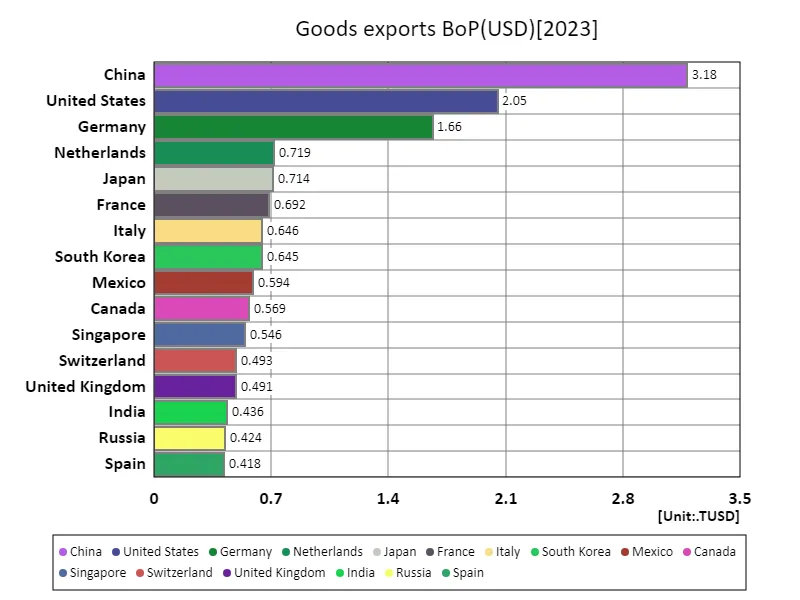

The maximum is 3.18TUSD of China, the average is 185GUSD, and the total is 21.1TUSD
Food exports (% of merchandise) (region, latest year)
Food exports (% of merchandise) data for 2023 shows that Latin America and the Caribbean is a hot region globally for food exports. This region recorded the highest overall rate and the average also remained high at 13.1%. This highlights the fact that Latin American and Caribbean countries have abundant resources in agriculture and fisheries, and that food exports, taking advantage of these resources, are an important economic activity. Consistent with past trends, Latin America and the Caribbean continues to be a major player in food exports. Notable export items include coffee, bananas, fruit, and seafood. Many of these countries have favorable climate conditions and soil conditions, and their agricultural productivity is high, which contributes to their high food export ratios. In addition, the high food export share of Latin America and the Caribbean indicates its competitiveness in international markets, but at the same time exposes it to the risks of price volatility and climate change. Economic diversification and the promotion of sustainable agriculture are key issues to improve the economic stability of these countries. Overall, Latin America and the Caribbean’s food export ratio reflects the specific characteristics of its economies, calling for efforts towards sustainable development and economic resilience across the region.

The maximum is 23.3TUSD of World, the average is 23.3TUSD, and the total is 23.3TUSD



Comments