Abstract
A high ratio of transportation services (services ratio) indicates a large share of transportation of imported goods. Ethiopia has the highest share at 74.8% because the country’s economy is highly dependent on imports. Developing countries like Ethiopia have limited domestic production capacity and therefore tend to be highly dependent on imports from outside. This will result in a higher ratio of transport services. A trend seen over the past few years is that African countries are becoming increasingly import-dependent, with transportation costs accounting for a large proportion of total import costs, especially in areas with less developed infrastructure. Ethiopia’s high service ratio can be attributed to its economic structure and underdeveloped infrastructure.
Transportation services (service ratio)
Countries with a high ratio of transport services to sold goods indicate a high reliance on imports. Haiti’s record of 91.3% in 1998 reflects its extreme import dependence and the high costs of transporting it. This high ratio reflects Haiti’s economy’s reliance on externally sourced products and very limited domestic production capacity. Over time, Haiti’s service ratio has declined to 78.4%, but it still remains high. These fluctuations are likely due to improvements in the domestic production base, developments in transportation infrastructure, or fluctuations in international trade. Overall, it can be seen that countries with a high transportation service ratio have a high proportion of imported goods and that transportation costs have a large impact on the economy.
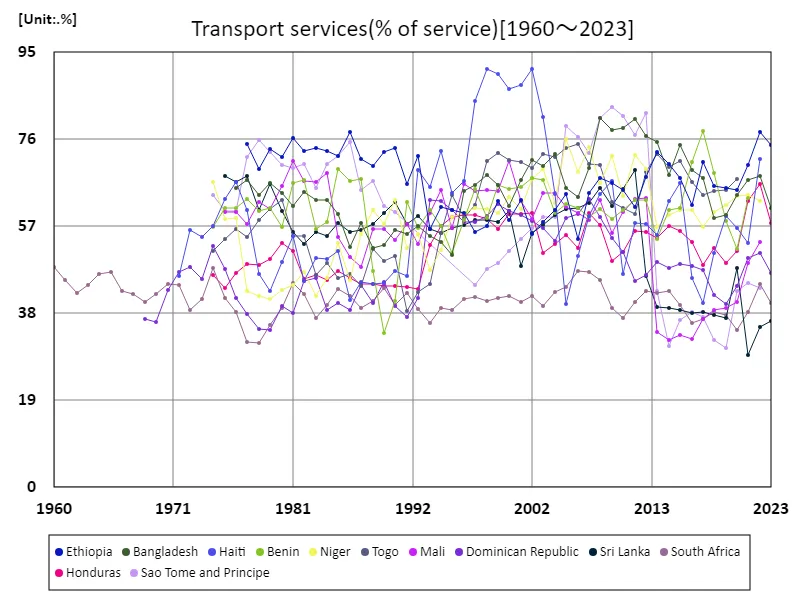

The maximum is 91.3%[1998] of Haiti, and the current value is about 78.4%
Transportation services (service ratio) (worldwide)
Countries with a high service ratio for transportation services indicate that the cost of transporting imported goods has a large impact on the overall economy. Haiti’s high ratio of 91.3 percent in 1998 reflects the country’s high reliance on imports. This was due to an insufficient domestic production base and imports being the main source of supply. The current decline in Haiti’s service ratio to 78.4% is likely due to changes in the country’s economic structure and improvements in transportation infrastructure. However, since the ratio remains high, it can be said that the economic structure dependent on imports remains deeply rooted. Overall, the trend over the past few decades has been that developing countries continue to experience higher transport costs, while the ratios change as economies grow and infrastructure develops.
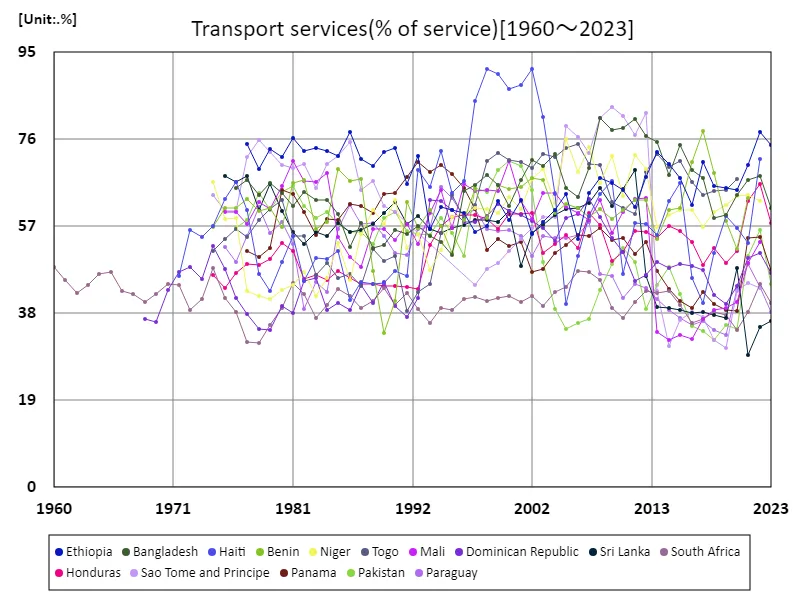

The maximum is 91.3%[1998] of Haiti, and the current value is about 78.4%
Transport services (service ratio) (World economy, latest year)
According to the 2023 data, Ethiopia recorded the highest service ratio for transportation services at 74.8%. This high ratio indicates that Ethiopia is highly dependent on transporting imported goods and its economy is highly dependent on imported goods. Developing countries like Ethiopia tend to have a higher proportion of transportation services as domestic production capacity is limited and imports are a significant part of the economy. With an overall average of 30%, transport services are a significant component of import costs for many countries, although there are a few countries with extremely high ratios, such as Ethiopia. The total figure of 3.33k% represents the aggregate ratio of transport services in the countries studied, and overall it shows that transport services play a certain role in the economy. Over the past few decades, the service ratio has fluctuated in developing countries due to infrastructure development and economic growth, but the cost of transport services still has a significant impact on the economy.
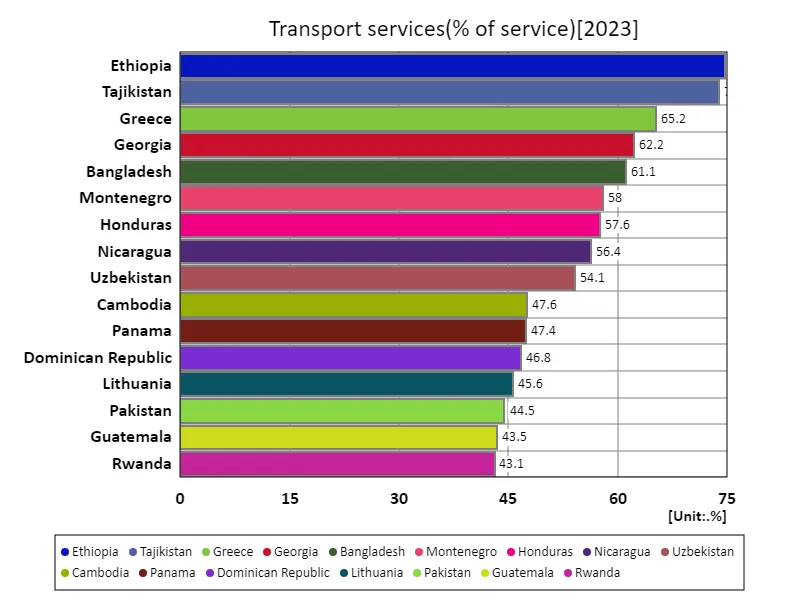

The maximum is 74.8% of Ethiopia, the average is 30%, and the total is 3.33k%
Transportation services (service ratio) (region, latest year)
In 2023 data, Eastern and Southern Africa recorded the highest proportion of transport services for sold goods at 42.3%. This high ratio indicates that these regions are highly dependent on transporting goods for sale, and is likely due to underdeveloped infrastructure and inefficiencies in trade. In developing regions of Africa, transportation networks are underdeveloped, meaning transportation costs have a significant impact on overall sales costs. While the overall average rate is 25.5%, the higher rates in Eastern and Southern Africa are notable and reflect the particular challenges faced in these regions. The total figure of 230% represents the total transport service ratio across all countries studied, indicating that transport costs play a significant role in the overall economy beyond national differences. Historically, the proportion of transport services has been high in developing regions, but this proportion is expected to decline as infrastructure improves and trade efficiency increases.
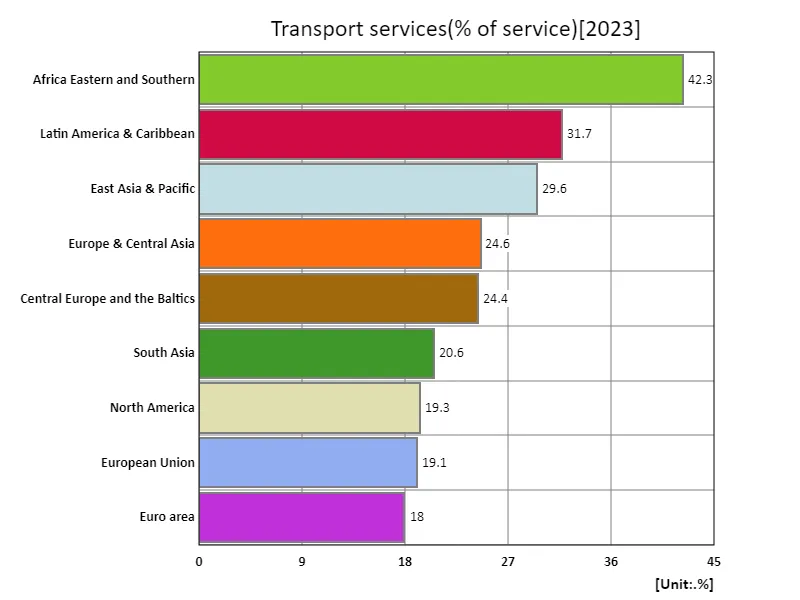

The maximum is 42.3% of Africa Eastern and Southern, the average is 25.5%, and the total is 230%



Comments