Abstract
Global merchandise imports are expected to reach USD 24.3 trillion in 2023, a significant figure compared to historical trends. The background to this growth is the advancement of globalization, the expansion of consumer markets, and the increasing complexity of international supply chains. A major factor is the increase in demand from rapidly growing emerging market countries. Countries such as China and India have significantly increased their imports as consumption increases, which has boosted the overall import bill. In addition, during the recovery period from the COVID-19 pandemic, disruptions to the supply chain and increased logistics costs have led to rising prices and an increase in import amounts. This has led to higher prices for imported goods and, as a result, an increase in the overall import bill. Additionally, there is growing global demand for advanced products, such as technology and energy resources, which is driving an increase in import bills. Thus, the increase in the value of world sales imports reflects fluctuations in the global economy and market dynamism. International trade trends and economic policies will continue to be important factors.
Sale Import(usd)
Looking back at data from 1960 to 2023, the value of world sales and imports has undergone significant change. In the 1960s, the scale of trade was relatively small, hovering around a few trillion USD, but it grew rapidly in the 1990s and 2000s with the advancement of globalization. Growth has been particularly remarkable since the 2000s, with global merchandise imports reaching a historic peak of 25.8 trillion USD in 2022. This rapid growth has been underpinned by trade liberalization, technological innovation, and the rapid growth of emerging market economies. Emerging economies such as China and India have significantly increased their import bills due to rapid industrialization and rising consumption. Another factor is the increasing complexity of global supply chains. However, by 2023, it will fall to USD 24.3 trillion, which is 94.3% of its peak. The decline is driven by high inflation in 2022, supply chain disruptions and economic uncertainty. In particular, the wave of economic recovery following the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions influenced trade trends. Overall, the value of imported goods sold shows a long-term growth trend and is expected to fluctuate in the future depending on economic conditions and international trade policies.
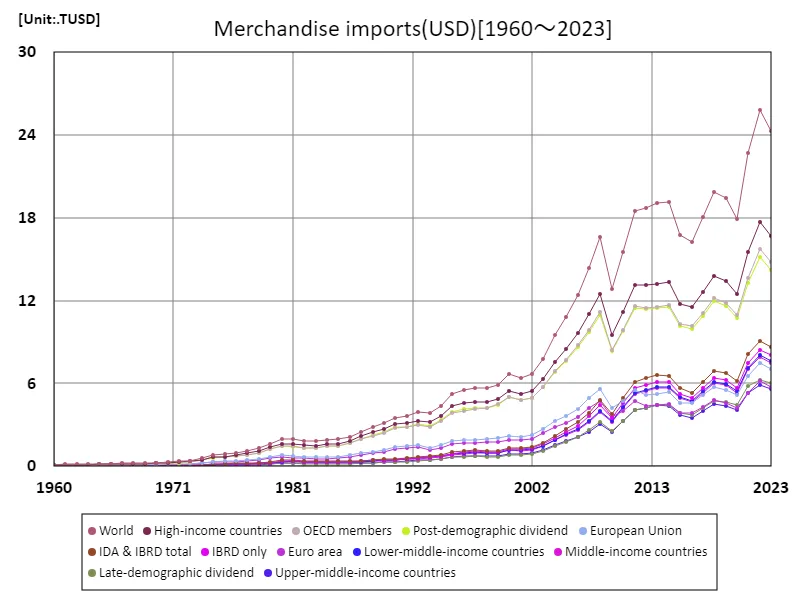

The maximum is 25.8TUSD[2022] of World, and the current value is about 94.3%
Merchandise Import(usd)(Worldwide)
From 1960 to 2023, the value of U.S. sales and imports has undergone significant changes. It will peak at 3.37 trillion USD in 2022, but will decline to 3.17 trillion USD in 2023, which is 94.1% of the peak. This fluctuation reflects the international influence of the American economy and changing trade patterns. In the 1960s, American imports were relatively low and policies were primarily aimed at protecting domestic industries. However, from the 1970s to the 1980s, imports increased with the progress of globalization, particularly from China and Southeast Asian countries. During this period, the American consumer market underwent a major transformation with the influx of cheaper products from countries with low manufacturing costs. Since the 2000s, US imports have grown even more, reaching a historic peak in 2022. The increase in imports during this period is due to rising consumption as well as demand for a wide range of goods, including technology products, consumer goods and energy resources. However, imports declined in 2023 due to geopolitical tensions, inflation, and supply chain issues. Fluctuations in U.S. import figures are indicative of economic globalization and its effects, and will continue to fluctuate in response to changes in international economic conditions and policies.
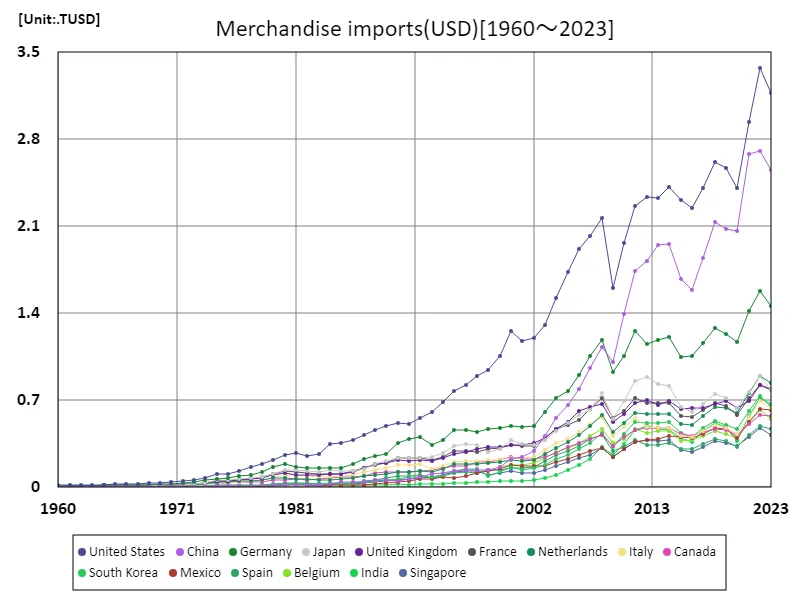

The maximum is 3.37TUSD[2022] of United States, and the current value is about 94.1%
Merchandise Imports (usd) (World Countries, Latest Year)
According to data for 2023, the United States’ merchandise imports were USD 3.17 trillion, accounting for a major portion of the world’s total imports. Total import value reached USD 23.2 trillion, with average import value of USD 121 billion. This data highlights the scale of international trade and American influence. Looking at trends over the past few decades, the United States has always been a major importer in the world, especially in terms of consumer goods and technology products. From the 1980s through to the 2000s, as globalization progressed, America began to outsource its manufacturing operations and import many manufactured products from abroad. This trend is driven by a maturing economy and an expanding consumer market. Meanwhile, global imports are expected to reach USD 23.2 trillion in 2023, high compared to previous peaks, although recent geopolitical tensions and supply chain issues are likely to impact import growth, with fluctuations expected. In particular, inflation and logistics issues are driving up import costs. Thus, U.S. imports remain an important player in the world economy, and global trade trends and economic policies will have a significant impact on future import patterns.
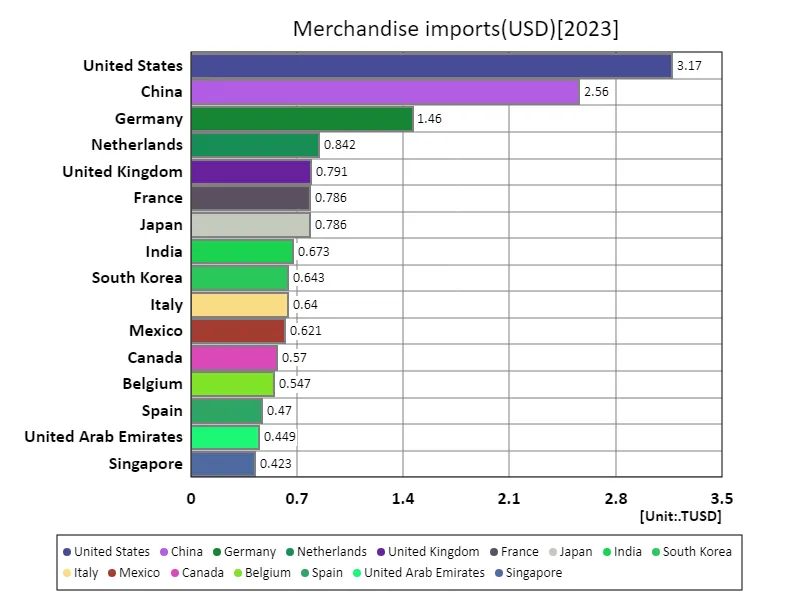

The maximum is 3.17TUSD of United States, the average is 121GUSD, and the total is 23.2TUSD
Merchandise Imports (usd) (region, latest year)
According to data for 2023, global merchandise imports will reach a total of USD 28.1 trillion, with the European Union (EU) recording the largest import volume at USD 7.04 trillion. The average import value is USD 1.88 trillion. The data shows the size and importance of European Union trade and highlights the EU’s central role in global economic developments. Looking at trends over the past few decades, the EU has been a major trading bloc for many years and plays an important role in global economic activity. As the EU expanded in the 1990s and 2000s, imports also increased, particularly of consumer goods, energy resources and technology products. The expansion of the EU single market has strengthened internal economic integration and promoted the diversification and scale of imports. The EU’s large import volume is also due to the high level of economic dependence among member states and its status as a major economic zone in the world. In contrast, the rise in global imports is a result of globalization, increasing consumption and more complex supply chains. However, in recent years, import patterns have fluctuated due to geopolitical risks and inflation. Thus, the EU’s large import volume reflects its economic size and international influence, and it will likely remain an important player in global trade.
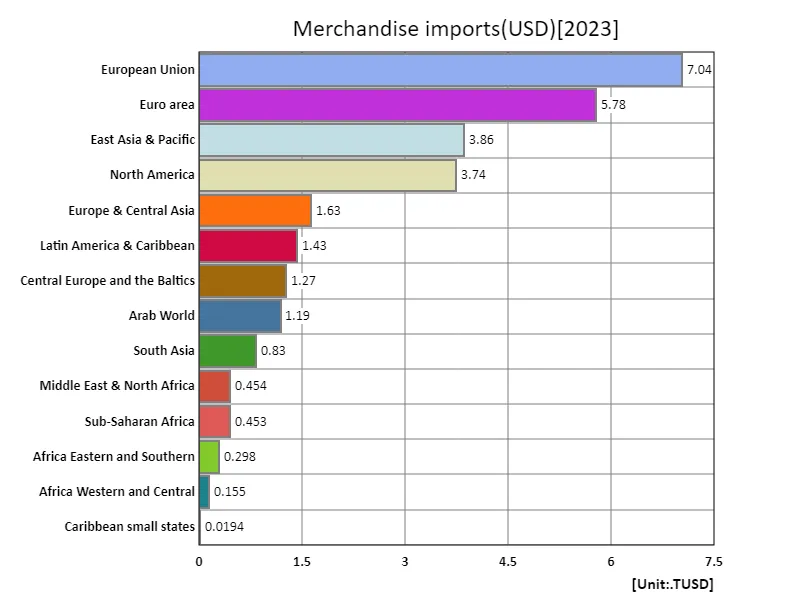

The maximum is 7.04TUSD of European Union, the average is 1.88TUSD, and the total is 28.1TUSD



Comments